垃圾综合处理压缩总体设计
小型垃圾压缩装置的设计
垂直式垃圾压缩装置总体的设计【优秀】【word+4张CAD图纸全套】【毕业设计】
【带任务书+鉴定意见+评阅表+外文翻译】【34页@正文16500字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】
中闸门.dwg
任务书.doc
总图.dwg
推铲.dwg
正文.doc
箱体总图.dwg
评阅表.doc
资源回收潜力分析研究——基于中国城市和农村生活垃圾的研究外文文献翻译.doc
鉴定意见.doc
任务书
论文(设计)题目: 垂直式垃圾压缩装置总体设计
一、主要内容及基本要求
查阅相关文献资料,熟悉了解大型城市生活垃圾处理压缩装置的发展现状和工作状况,并重点观察垃圾处理压缩装置的结构,对垃圾处理压缩装置进行整体结构设计及分析。
要求:
1、查阅相关资料,大致了解本次设计要研究的具体内容;
2、相关参数:装机容量380v,7.5kw; 举升高度3.0m(箱顶离地面高);占地面积6.2m*3.3m;最大压紧力100t;系统油压25MPa ;垃圾块外形尺寸:宽1900×长1650×高1400 mm /单块;垃圾压缩密度大于0.92吨/立方米;
3、若干图纸;
4、撰写毕业设计说明书;
5、外文文献翻译,字数3000字以上。
二、重点研究的问题
垃圾综合处理压缩总体设计。
三、进度安排
序号各阶段完成的内容完成时间
1查阅资料、调研第1-2周
2开题报告、制订设计方案第3周
3方案(设计)第4-5周
4垃圾综合处理压缩总体设计第6-7周
5写出初稿,中期检查第8-9周
6修改,写出第二稿第10-11周
7写出正式稿第12-13周
8答辩第14周
四、应收集的资料及主要参考文献
李国建、赵爱华、张益主编.城市垃圾处理工程.北京:科学出版社2003
宁平主编 固体废物处理与处置:搞等教育出版社2007
李传统主编 现代固体废物综合处理处理技术:东南大学出版社2000
路甫祥.液压气动技术手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社2002
国家环境保护局. 21世纪环境保护议程. 北京:中国环境科学出版社1995
徐国华.城市垃圾问题及处理对策[J].环境科学与管理2006
重伟,刘树道.全液压垃圾破碎机液压系统的设计[J].机床与液压2003
杨先海.城市生活垃圾压缩和分选技术及机械设备研究[D].西安:西安理工大学2004
张利平.液压传动系统及设计[M].北京,化学工业出版社2005
董涛.城市生活垃圾压缩技术及设备研究[D].淄博:山东理工大学,2003
Bridgewater, A. V. Refuse composition projection and recycling technology. Retour and Conservation, 1998
目录
摘要1
ABSTRACT2
第一章 绪论3
1.1垃圾压缩装置的简介3
1.1.1垂直式垃圾压缩装置3
1.1.2压装式垃圾压缩装置3
1.1.3小型垃圾压缩装置3
1.2课题研究背景及意义4
1.2.1课题研究背景4
1.2.2课题研究意义6
1.3课题研究现状及存在问题6
1.3.1研究现状6
1.3.2存在问题7
1.4本文的主要研究内容8
1.5本章小结8
第二章 垂直式垃圾压缩装置的结构设计9
2.1垃圾压缩装置形式的确定9
2.1.1城市生活垃圾压缩装置的基本类型9
2.1.2垃圾压缩装置整体方案的确定10
2.2垂直式垃圾压缩装置的总体设计11
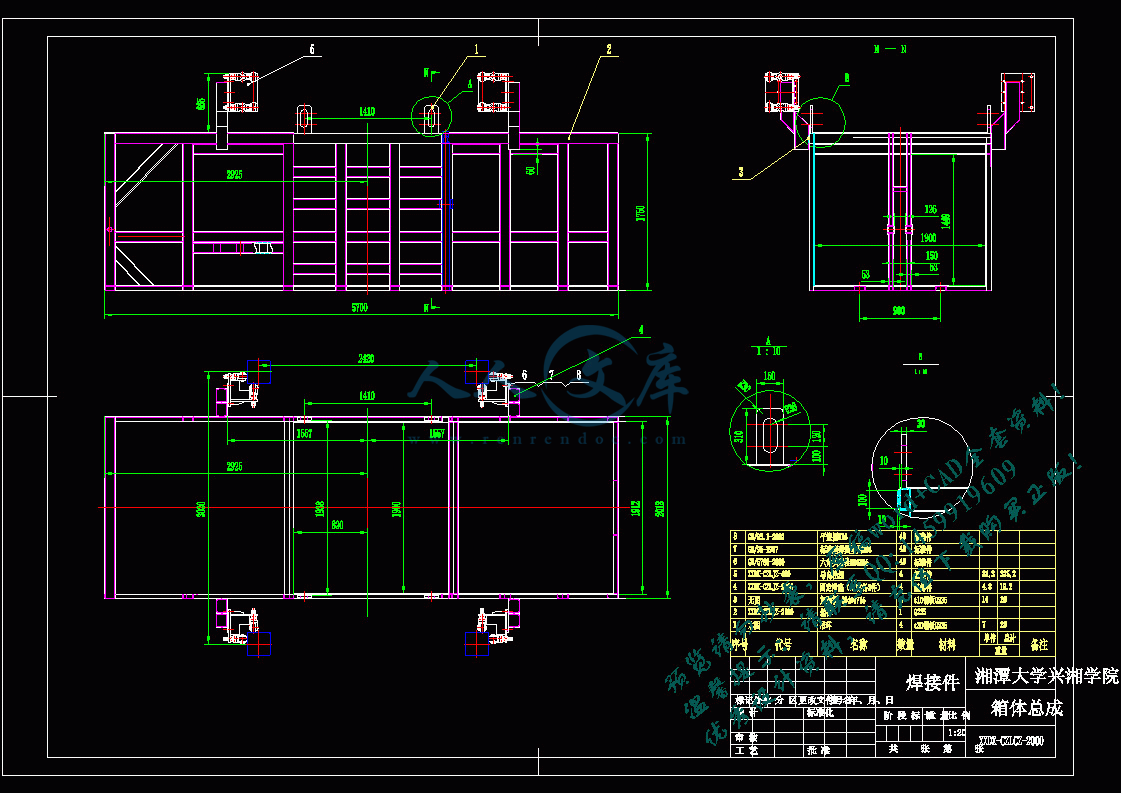
2.3垃圾箱总成的设计12
2.4机架的设计13
2 .5压力装置的设计14
2.6三联液压缸的设计15
2.6.1液压缸工作压力的确定16
2.6.2液压缸内径D及活塞杆直径d的确定16
2.6.3液压缸壁厚及外径的计算18
2.6.4液压缸工作行程和缸体长度的确定20
2.6.5液压缸结构形式的确定20
2.7本章小结21
第三章 垂直式垃圾压缩装置液压传动系统的设计22
3.1垂直式垃圾压缩装置液压系统的基本要求22
3.2液压系统原理设计22
3.2.1阀和基本回路22
3.2.2压头装置液压系统设计23
3.2.3推板机构液压系统设计24
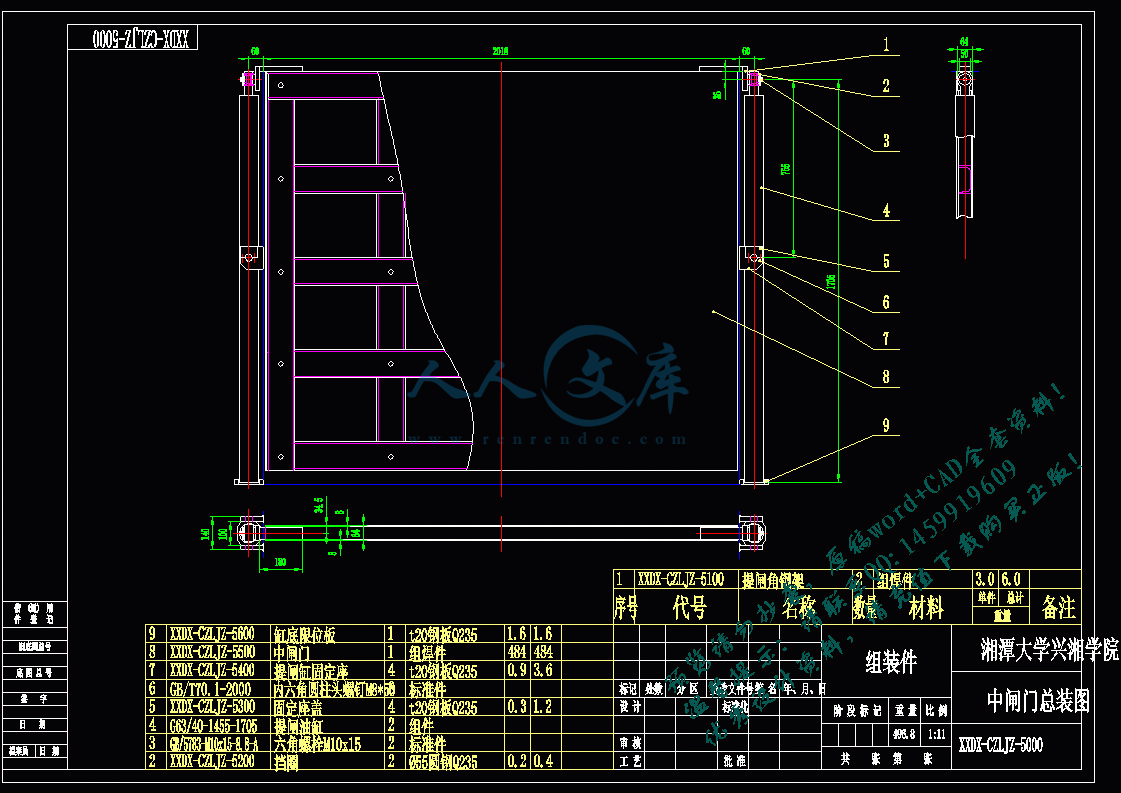
3.2.4中门机构液压系统设计25
3.2.5整个装置的液压系统26
3.3部分参数的选择与计算27
3.3.1系统压力(p)与流量(q)的确定27
3.3.2系统功率的计算与电动机的选择27
3.3.3液压泵选择及排量计算27
3.4液压传动系统的主要特点28
3.5本章小结28
第四章 全文总结与展望29
4.1全文总结29
4.2展望29
参考文献30
致谢31
附件32
垂直式垃圾压缩装置的设计
摘要
随着城市生活垃圾数量的不断增加,实行生活垃圾压缩转运势在必行。垂直式垃圾压缩装置是垃圾中转站的关键、核心设备之一,其主要功能是利用液压系统的驱动将收集到中转站的垃圾压缩成块,实现垃圾减容,能增大转运量,提高转运效率。
本文以垂直式垃圾压缩装置为研究对象,对其进行了结构设计和液压系统设计。论文的主要工作如下:
1.综合分析比较各类垃圾中转站的优缺点,确定了本课题的研究对象的工作环境——垂直式压缩垃圾中转站;
2.对垂直式垃圾压缩装置的整机结构及垃圾箱总成、机架、压力装置及其液压系统的液压缸进行设计和计算;
3.根据垃圾压缩装置的实际工作要求,对各机构和整机的液压系统原理进行了设计,选择与计算了部分元件的关键参数,使液压系统工作可靠、操作简便。
关键词:垃圾压缩装置,液压系统,液压缸
VERTICAL OF PRESSURE-TYPE GARBAGE COMPACTORS
ABSTRACT
With the increasing number of municipal solid waste, the implementation of domestic refuse compression transfer is a must. Pre-press type garbage compactors are vertically compressed rubbish transfer station key, one of the core facilities, its main feature is the use of hydraulic system driven rubbish compressed into blocks that are collected into a transit point, achieving the waste volume reduction, can increase transit capacity, improving transit efficiency.
Based on the vertical pre-loading type garbage compressor as the research object, on the structure design and hydraulic system design. Paper's main work is as follows:
Firstly, the comprehensive analysis and comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of all kinds of waste transfer station, determine the research object of this topic work environment - pit vertical compression pre-loading type transferring waste transfer station;
Secondly, for vertical pre-loading type rubbish compressor machine structure and the assembly, frame, pressure device and the hydraulic system of hydraulic cylinder design and calculation;
Thirdly, according to the actual work requirements of garbage compressor, the institutions and the machine hydraulic system principle of design, selection and calculation of some components of the key parameters, make the hydraulic system reliable operation, easy operation.
KEY WORDS:the refuse compactor, the hydraulic system, the hydraulic cylinder
第一章 绪论
1.1垃圾压缩装置的简介
垃圾压缩装置是实现垃圾压缩减容的主要设备之一,亦是垃圾转运站的主要处理设备。垃圾压缩装置是垃圾中转站的主要设备,是一种由液压系统控制的将收集来的垃圾进行压缩,以减少垃圾体积的机械。小型垃圾压缩装置处理垃圾的效率低。中、大型的垃圾压缩装置的压缩容量虽然大,但是需要建专门的大型卸料平台,占地面积较大,土建造价也很高。垃圾压缩装置分为以下三种。
1.1.1垂直式垃圾压缩装置
垂直式垃圾压缩装置的压缩力巨大,压缩彻底,压缩比率高,主要用于日处理要求很高的大中型垃圾转运站。
垃圾在密封压缩腔内被压成块状,然后一次性或分三次推入垃圾集装箱。
结构可靠,因摩擦而易损的配件易于调整及更换。
液压/电气系统可进行自动或手动控制,操作简易且易于维修。
垃圾压缩时不需转运车集装箱配合,更有效地提高转运效率。
可进行重量及容积的准确控制,控制转运车辆装载量。
压缩比大,压缩效率高,处理垃圾能力非常强。
适合于大中型垃圾转运站配套使用。
1.1.2压装式垃圾压缩装置
压装式垃圾压缩装置的压缩能力适中,主要用于日处理要求较高的中型垃圾转运站。
垃圾被压缩装置直接推入垃圾集装箱中压缩,待垃圾箱中垃圾重量达到预设值,压缩周期结束。
结构可靠,因摩擦而易损的配件易于调整及更换。
液压/电气系统可进行自动或手动控制,操作简易且易于维修。
压缩比大,压缩效率高,处理垃圾能力非常强。
适合于大中型垃圾转运站配套使用。
参考文献
【1】 李国建、赵爱华、张益主编.城市垃圾处理工程.北京:科学出版社2003
【2】 宁平主编 固体废物处理与处置:搞等教育出版社2007
【3】 李传统主编 现代固体废物综合处理处理技术:东南大学出版社2000
【4】 路甫祥.液压气动技术手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社2002
【5】 国家环境保护局. 21世纪环境保护议程. 北京:中国环境科学出版社1995
【6】 徐国华.城市垃圾问题及处理对策[J].环境科学与管理2006
【7】 重伟,刘树道.全液压垃圾破碎机液压系统的设计[J].机床与液压2003
【8】 杨先海.城市生活垃圾压缩和分选技术及机械设备研究[D].西安:西安理工大学2004
【9】 张利平.液压传动系统及设计[M].北京,化学工业出版社2005
【10】 董涛.城市生活垃圾压缩技术及设备研究[D].淄博:山东理工大学,2003
【11】 Bridgewater, A. V. Refuse composition projection and recycling technology. Retour and Conservation, 1998
【12】 陈召国,曾经梁.全液压压块式垃圾中转站液压系统的设计,液压与气动,2005
【13】阮志华.城镇垃圾压缩装置的研制[J].机械工程师,2002,


 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号