【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
[全部文件] 那张截图中的文件为本资料所有内容,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
摘要
排泥机械是在自来水厂和污水处理厂中配合沉淀池使用的,它是重要的排泥专用设备。排泥机械的形式随工艺的条件与池形的结构而有所不同,目前常用的排泥机械可分为平流式(矩形)沉淀池排泥机和辐流式(圆形)排泥机两大类。刮泥机主要有周边传动式、中心传动式、矩形平流池桁车式、链传动式等。它是排泥机械中的一种常见设备,它是沉淀池不可缺少的设备。一般采用铝合金,不锈钢或防腐处理型钢制作,具有电动提肥,过载保护、撇渣、刮泥、虹吸排泥过程监控,电气联锁等特点,动力消耗低、防腐性能强、吸泥量可调、传动平稳、运行可靠。
本设计研究的刮泥机为周边传动式。并将可编程序控制器(PLC)应用于控制系统中,极大的简化操作过程,提高运行稳定性。具有结构简单,运转连续,管理方便等一系列优点。
关键词:可编程控制器;全自动运行;环保;刮泥机
Abstract
Arranges the putty machinery is in the Waterworks and the Sewage treatment plant,the coordinate sedimentation pond use,it is the important special purpose equipment. Arranges the putty machinery's form differs from along with the craft condition and the pond structure,at present the commonly used platoon putty machinery may divide into the advection type (rectangle) a sedimentation pond row of putty machine and the spoke class type (circular) the row of putty machine two broad headings. The mud scraper mainly has peripheral transmission type,central transmission type,the rectangular advection pond clothes rack car type,the chain drive type and so on. It is in the row of putty machinery's one kind of common equipment; it is the sedimentation pond essential equipment. Generally uses the aluminum alloy, the stainless steel or the antiseptic treatment section manufacture,has raises electrically operated fat, the over-load protection, casts aside the dregs,to blow the putty,the rainbow to attract the row of putty process monitoring,characteristics and so on electrical interconnection, the power consumption is low,the antiseptic property strong,attracts the putty quantity adjustable,the transmission to be steady,the movement is reliable.
This design research mud scraper for peripheral transmission type. And applies programmable controller (PLC) in the control system,the enormous simplification operating process,enhances the movement stability.Has the structure to be simple,the revolution is continual,manages the convenience and so on a series of merits.
Keywords:PLC Completely automatic movement environmental protection Mud scraper
目 录
1 绪论1
1.1 我国的环保形势1
1.2 常用的的污水处理工艺简介2
1.2.1活性污泥工艺2
1.2.2氧化沟工艺2
1.2.3 A-O法及A-B法2
1.2.4 SBR法2
1.3 刮泥机简介及其在污水处理中的地位3
1.4 我国现存刮泥机的种类,各自的应用场合和优缺点3
1.5 本课题研发的刮泥机简介5
1.6 研究意义6
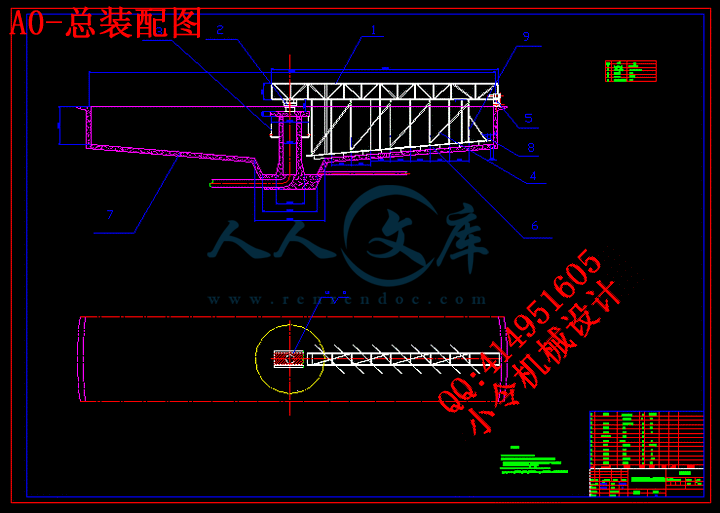
2 刮泥机总体设计7
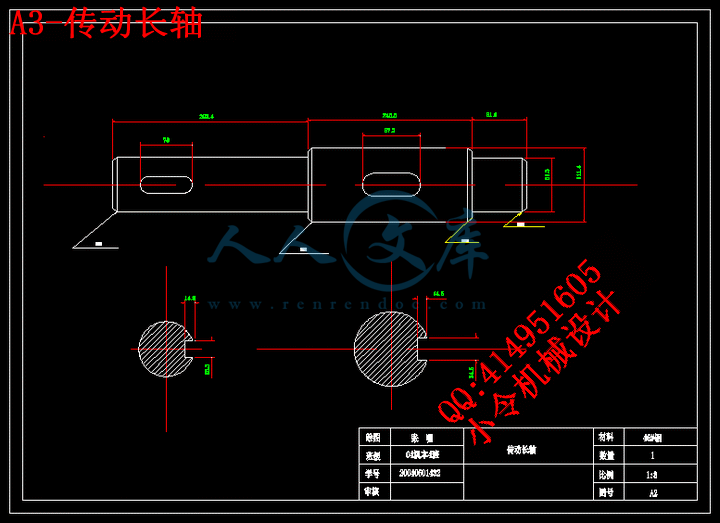
2.1 本课题刮泥机的设计参数7
2.2 周边传动的总体构成7
2.2.1 全跨式7
2.2.2 半跨式7
2.2.3 中心旋转支座9
2.2.4 撇渣机构及刮板布置10
2.3 动力系统总体设计11
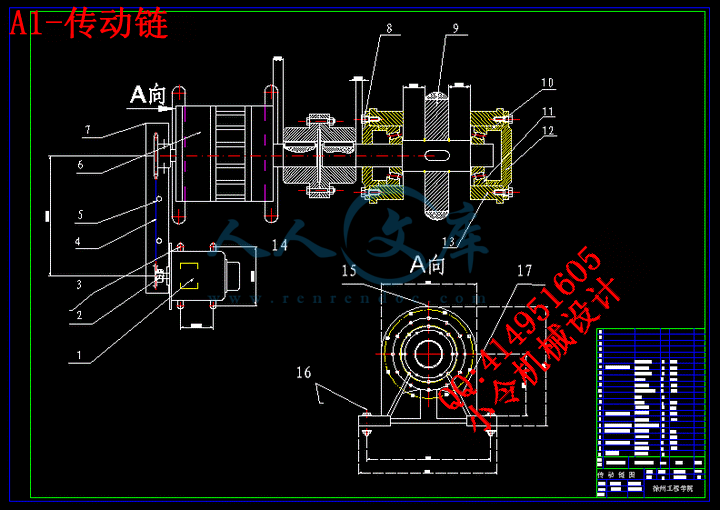
2.3.1 工作原理11
2.3.2 传动机构各部分的组成12
2.4 初沉池的设计12
2.4.1 高密度澄清池概况12
2.4.3高密度澄清池的三种类型13
2.4.4高密度澄清池的简介13
2.4.5初沉池设计参数13
3 动力系统设计与计算15
3.1 传动装置设计的要求15
3.2 电动机的选择15
3.2.1 选择合适的电动机16
3.2.2 电机驱动功率的计算与选择16
3.3 联轴器的设计18
3.3.1联轴器的分类18
3.3.2联轴器选择应考虑的问题19
3.3.3联轴器的选择19
3.4泵的选择20
3.4.1进水泵的选择20
3.4.2出水泵的选择21
3.5链轮的设计22
3.5.1链轮对齿形要求22
3.5.2链轮的主要设计参数22
3.5.3链轮的结构型式22
3.5.4链轮的材料要求22
3.6传动轴的设计与计算23
3.6.1 轴的概述23
3.6.2 轴的材料23
3.6.3 轴的强度计算23
3.6.4 轴的刚度计算24
3.6.5刮泥机传动轴的计算24
4 PLC控制系统的设计26
4.1 PLC控制系统的设计的主要内容26
4.2 PLC编写控制系统程序设计的步骤26
4.3 PLC的选择27
4.3.1 PLC容量的估算方法27
4.3.2 PLC存储容量的估算方法27
4.3.3 数字I/O点数与模块的确定27
4.3.4 输入模块的确定28
4.3.5 输出模块的确定28
4.3.6 PLC选型确定28
5电气控制系统的设计29
5.1电气控制系统的意义29
5.2绘制电气控制图的要求29
5.3刮泥机动力系统泥机总体方案29
5.4 主电路系统的设计30
5.4.1 控制系统的要求30
5.4.2 主电路的设计31
5.5 PLC外部接线设计31
5.6 交流控制线路设计33
5.7 主要参数设计34
结论35
致谢36
参考文献37
附录38
英文原文38
中文翻译44
1 绪论
1.1 我国的环保形势
作为发展中的社会主义国家,我国人民在现代化建设的过程中,面临比世界其他国家更为严峻人口、资源和环境形势。沉重的人口负担,人均资源不足,环境状况恶化,严重影响着党和政府发展经济的宏观决策,也影响着人民群众生活水平的提高,成为制约我国社会主义建设的首要问题。
改革开放三十多年来中国社会公众和各级领导干部的环保意识得到大幅提高,中国的社会环境、自然资源在很大程度上得到改善。但是,目前中国已经进入工业化中期和城市化迅速发展的时期,从发达国家的经历来看,这是消耗资源最多,对环境破坏最大的时期。为了社会的可持续发展,中国政府提出了全面、协调、可持续发展的科学发展观。改革开放,特别十一届四中全会以来,我国的环境保护工作有了长足的发展。
1.明确了环境保护为基本国策之一的地位,制定了中国自己的可持续发展战略。
1992年联合国环境与发展大会之后,我国率先提出了《环境与发展十大对策》,指定《中国21世纪议程》,《中国环境保护行动》等文件,实施可持续发展战略已成为国民经济和社会发展的基本指导方针。
2.建立了更为 的环境管理体制和法律机制
经过十多年的努力,在全国范围内初步建立起了环境保护部门监督管理,各有关部门分工负责的环境管理体系以及响应的环境监测、监理、统计、科研、宣传、教育体系。
到1997年,我国相继颁布了《环境保护法》等6部专门的环境法律,资源保护法律9部,环境行政法规28件,环抱部门发布环境规章70余件,环境标准390项。环保已经从主要依靠行政手段向着利用法律手段转移。
3.城市环境整治和工业污染防治取得了明显成效,环境保护已经从末端治理转变到源头控制。
4.环境外交和国际合作日益活跃
我国积极开展环境外交,参与各项重大的国际环境事务,在国际环境与发展领域中发挥月来越大的作用;签署并批准了《保护臭氧层维也纳公约》,《联合国气候变化框架会议》,《生物多样化公约》等多项国际环境公约。
每年,政府还投入了大量资金用于环境治理。其中与人民生活休戚相关的环保设备得到了极大的关注.在国内环保需求的拉动下,我国环保设备行业有了明显的进步。“十五”期间,全行业工业总产值同比增幅在15%以上,有的重点企业高达37%。其中,2006年水污染防治设备的产量与2005年相比增长6倍;固体废弃物处理设备的产量增加了31.18%;环境监测仪器的产量2006年也有了明显回升。但是,由于国产环保设备及仪器仪表档次不高,我国各行业的节能减排受到一定程度的制约。比如,国内开发的污染在线监测仪器仪表尚未完全过关,进口监测仪器仪表又价格太贵。因此,除关键必要部位外,很多大型化工企业只好采用人工取样、分析,一定程度上影响了环保技术的发展和治理水平的提高。
随着排污总量控制的推行、污染物排放标准的加严和清洁生产的实施等,化工环保设备的性能和技术需要进一步优化,提升产品的档次。质量上的缺陷、材料性能和质量的不适应,以及少数产品适用性不佳等,是影响化工环保设备质量稳定的重要因素,必须加以改进提高。同时,提高高新技术产品比例和重大技术装备的成套水平,推进关键技术创新,发展某些领域缺乏的技术装备、高效低成本的环保机械产品,是当前和今后提高产品品种满足度的重要内容。某些重点环境工程的质量较差,甚至建成后不能运行,出现问题的原因涉及工程设计、成套能力、产品质量及工程管理诸多方面,同样应引起重视。据了解,目前化工环保设备的市场需求热点是:污水处理成套设备、再生水(中水)回用成套设备等。此外,清洁生产的众多领域都将是环保设备新的发展空间




 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号