KCJ25型柏油路面开槽机设计【4张图纸】【优秀】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:(预览前20页/共22页)
编号:453863
类型:共享资源
大小:2.50MB
格式:RAR
上传时间:2015-07-08
上传人:小***
认证信息
个人认证
林**(实名认证)
福建
IP属地:福建
46
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
kcj25
柏油
路面
开槽
设计
图纸
优秀
优良
- 资源描述:
-
KCJ25型柏油路面开槽机设计
摘要
开槽机主要用于沥青、水泥路面裂缝病害处治时的开槽作业,通过特质刀片快速将不规则裂缝整理成均匀的凹槽,形成新的结合面。
我国在过去的几十年中,高速公路建设的速度很快,规模也达到了顶峰时期,并且在将来的一段时间中也将持续的发展,同时公路运输完成的运输量也在迅速的增加。由于我国气候和车辆超载严重等诸多原因,新修的柏油路通车几年就产生了车辙、开裂、泛油、坑槽等一些早期损坏现象。鉴于此,对高速公路早期损坏进行小型维修是很必要的,特别是对裂缝和坑槽的修补,可以延长公路的寿命,对社会和经济效益都有很大的作用。而对这些局部损坏路面的修复又主要是通过灌封填补实现的。因此,一台高效率的柏油路面开槽机是十分必要的。目前开槽机广泛应用于公路建设及市政工程中的新路面收缩缝的切割,以及旧混凝土路面维修切割和开槽切割作业。其工作原理可以简单地描述为通过动力驱动刀轴带动刀片运动完成开槽作业。本文较为详尽地描述了KCJ25柏油路面开槽机的开发设计过程。
关键词:开槽机,柏油路面,损坏,修补
KCJ25 Asphalt Slotting Machine Design
Author:jinhe
Tutor:xuedongbin
Abstract
Slotting machine is mainly used for asphalt, cement pavement cracks Disease Treatment slotting operations, irregular cracks through the characteristics of the blade quickly organized into a uniform groove to form a new joint surface.
China in the past few decades, the speed of the highway construction will soon scale reached its peak period, and will continue in the future period of time the development of transport by road transport also increased rapidly.Serious overloading and so many reasons due to our climate and vehicles, the newly built paved road open to traffic a few years to produce a rutting, cracking, weeping, pits some of the early damage phenomenon. View of this, the highway early damage is necessary to carry out minor repairs, especially the repair of cracks and trenches, can extend the life of the road, has a significant role in the social and economic benefits.Repair for localized damage to the road is mainly achieved by potting to fill.Therefore, an efficient asphalt slotting machine is very necessary. Slotting machine is widely used in road construction and municipal projects in the new pavement contraction joint cutting, as well as the maintenance of the old concrete pavement cutting and slotting cutting operation.Its working principle can be simply described as driven by power-driven blade shaft blade movement slotting operations.More detailed description of the KCJ25 asphalt slot machine development and design process.
Key words:Slotting machine,Asphalt,Damage,Repair
目录
1绪论1
1.1课题的背景及目的1
1.2国内外研究状况2
1.3课题研究方法2
1.4论文构成及研究内容3
2 总体方案设计4
2.1设备介绍4
2.1.1 开槽机的工作原理和组成4
2.1.2开槽机的分类4
2.1.3 开槽机的作用5
2.1.4 应用限度5
2.2 设计要求5
2.3设计方案分析6
2.4刀具分析6
2.4.1刀具材料的选择6
2.4.2刀盘整体构造的确定7
2.4.3切削刃几何角度的选择8
2.5带传动的设计8
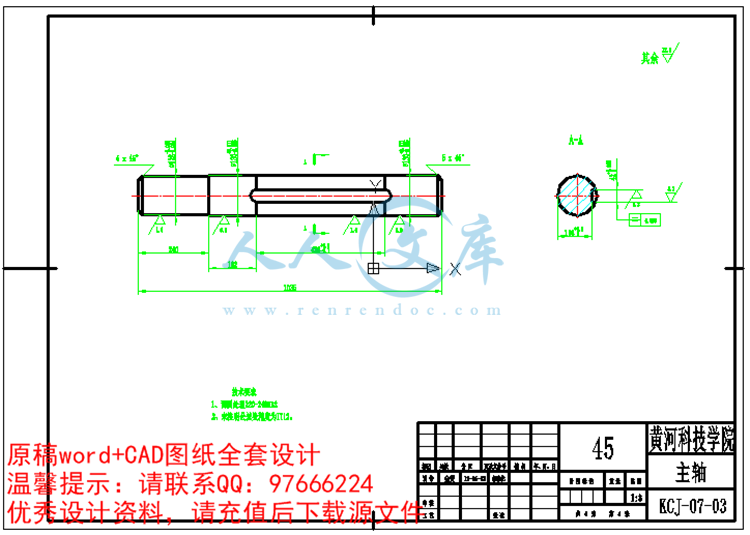
2.6轴的设计12
结论16
致谢17
参考文献18
1绪论
1.1课题的背景及目的
近年来国内公路建设发展迅速,且不说绝大多数城市干道和城际通道几乎全部以公路为主,继国家实施“村村通(公路)”政策以来,广大农村地区的柏油马路更是如雨后春笋般被建出来。据调查,截至到2009年底,全国公路总里程达到230万公里,其中等级公路里程159.18万公里,占公路总里程的82.5%。按公路技术等级分,各等级公路里程分别为:高速公路41005公里、一级公路38381公里、二级公路246442公里、三级公路344671公里、四级公路921293公里,等外公路338752公里。由于沥青(柏油)路面具有足够的力学强度和一定的弹性、塑性变形能力,有高度的减振性,行车平稳舒适、噪声低,且不扬尘等特点,已修和待建的交通主干道,特别是高速公路大部分为沥青路面。虽然国内外对柏油路面的修筑进行了不懈的研究和总结,施工技术已较为完善,并得到了广泛的应用,但在存在着气候和交通荷载条件恶劣,车辆超载严重等问题,新修的柏油路通车几年就发生了车辙、严重丌裂、泛油、坑槽等一些早期损坏现象。其实即便是在筑路技术已经非常发达的国家,也难以避免马路破损的问题,因为它们毕竟是暴露在大自然的带状工程结构物,长期经受着日晒、雨雪、醅热、严寒和冻融,并承受着频繁交通瞬时动荷载的反复作用。据统计,高等级公路的一般设计寿命为12~15年。




- 内容简介:
-
1 黄河科技学院 毕业设计开题报告表 课题名称 KCJ25 型柏油路面开槽机设计 课题来源 教师拟订 课题类型 AX 指导教师 薛东彬 学生姓名 金贺 专 业 机械设计制造及其自动化 学 号 080105655 一、调研资料的准备 根据任务书的要求,在做本课题之前,查阅了与该课题相关的资料,有:机械制图、机械设计、 力学 、机械制造工艺学、 CAXA 制造工程师基础教程与毕业设计指导手册等一系列与设计相关的材料。 二、设计的目的与要求 毕业设计是大学教学中最后一个实践性教学环节,通过该设计过程,可以 检验我对所学知识融会贯通的程度,同时培养我处理工程中实际问题的能力,因此意义特别重大。 利用 CAXA 制造工程师软件先对 开槽机进行设计,并完成其装配图与部分零件图的设计 。 三、设计的思路与预期成果 1、设计思路 分析国内外柏油路面开槽机发展和应用的情况,结构类型和功能特点,结合国内开槽机的实际情况拟定开槽机的总体方案。 首先完成总体机械结构的设计,要考虑到性能稳定、运转灵活、安全可靠、节能环保;然后完成传动机构的设计,选择合适的传动机构,对从汽油机到主轴的传动机构进行设计和计算;最后对支撑部件进行设计。 2、预期的成果 ( 1) 完成文献综述一篇,不少与 3000 字,与专业相关的英文翻译一篇,不少于 3000 字; ( 2) 完成内容与字数都不少于规定量的毕业设计说明书一份; ( 3) 绘制装配图,部分零件图; ( 4) 刻录包含本次设计的所有内容的光盘一张。 四、任务完成的阶段内容及时间安排 1 3 周 完成文献综述、开题报告及英文资料翻译,掌握 CAXA 软件应用功能,完成毕业实习。 4 5 周 对 KCJ25 型柏油路面开槽机进行总体、局部、零件结构的设计及计算。 6 9 周 用 CAXA 软件绘制总装图、典型零件图。 10 11 周 编写设计说明书,进一步修改完善毕业设计,准备并完成毕业答辩稿。 12 周 毕业答辩。 nts 2 五、完成设计所具备的条件因素 我已修完机械制图、机械设计、机电一体化技术、机械制造工艺学、机械制造技术基础、数控原理与系统、数控机床构造、 CAXA 制造工程师基础教程及毕业设计指导等课程,同时借助图书馆的相关文献资料并查询相关的网络等资源。 指导教师签名: 日期: 课题来源:( 1)教师拟订;( 2)学生建议;( 3)企业和社会征集;( 4)科研单位提供 课题类型:( 1) A 工程设计(艺术设计); B 技术开发; C 软件工程; D 理论研究; E 调研报告 ( 2) X 真实课题; Y 模拟课题; Z 虚拟课题 要求( 1) 、( 2)均要填,如 AY、 BX 等。 nts 目 录 1任务书 1 2开题报告 2 3指导教师评阅表 4 4主审教师评审表 5 5 毕业设计(论文)答辩评审与总成绩评定表 6 6毕业设计说明书 7 7文献综述 30 8文献翻译 40 9光盘 10 设计图纸或实验数据记录 nts 单位代码 0 2 学 号 080105655 分 类 号 TH6 密 级 秘密 毕 业设计 文献综述 院(系)名称 工学院机械系 专业名称 机械设计制造及其自动化 学生姓名 金贺 指导教师 薛东彬 2012 年 3 月 10 日 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 1 页 KCJ25 型柏油路面开槽机设计 摘要 本文介绍了柏油路面开槽机,开槽机主要用于沥青、水泥路面裂缝病害处治时的开槽作业。通过特质刀片快速将不规则裂缝整理成均匀的凹槽,形成新的结合面。优化灌缝材料与缝槽的接触层面,加强灌缝材料与缝槽侧壁粘结的紧密性。首先介绍了开槽机在国内外的发展现状 ,并对开槽机的动力机构与传动机构进行了分析 ,此 外还介绍了平面连杆机构。 关键词 : 开槽机,裂缝 ,凹槽 1 公路养护机械在国内外的发展现状 1.1 公路养护机械化在国内的发展状况 20 世纪 60 年代初,我国公路建设处在以砂石路面为主的时代,可供公路养护用的机械很少,加上当时国家经济条件的限制,对公路养护投入的资金严重不足,公路养护大多以人工为主。改革开放以后,特别是高速公路的发展,为引进先进的养护机械创造了机遇。但是,我国的养护机械无论是产品性能还是品种、数量、质量都难以满足我国高等级公路维修养护作业的需要,部分类型的公路养护机械国内还不能自主生产。国内缺少 混凝土切割理论,制约着切割工具的设计、机械的效率及刀具磨损,影响机器的工作与性能。因此,切割技术发展缓慢。 1.2 公路养护机械化在国外的发展状况 经济发达国家很早就发展了公路的施工建设,养护管理工作同时也跟上了建设的步伐,由于日常养护工作做得好,这些国家高速公路虽然建成使用了近半个世纪,但至今仍在使用。他们在公路养护和管理方面有较完善的质量保证体系,普遍建立了公路养护计算机管理系统,并配备了先进的养护机械,在不断发展养护机械的同时,注重养护施工工艺与养护材料的研究与开发工作。近几年来,发达国家更加重视养护管 理系统的建设,利用开发出的公路路况诊断检测、评估设nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 2 页 备等多种养护辅助系统,实现对公路状况的自动检测与数据的采集,建立公路信息管理数据库,对公路路况实施动态管理,达到以预防为主的养护目的。 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 3 页 2 开槽机的结构 2.1 开槽机的动力机构 开槽机的动力机构选用汽油发动机,它 是以汽油作为燃料的发动机。由于汽油粘性小,蒸发快,可以用汽油喷射系统将汽油喷入气缸,经过压缩达到一定的温度和压力后,用 火花塞 点燃,使气体膨胀做功。汽油机的特点是转速高,结构简单,质量轻,造价低廉, 运转平稳,使用维修方便。 2.1.1 小型汽油机一般系 统组成 ( 1)曲轴连杆系统包括活塞、连杆、曲轴、滚针轴承、油封等。 ( 2)机体系统包括缸盖、缸体、曲轴箱、消声器、防护罩等。 ( 3)燃油系统包括油箱、开关、滤网、沉淀杯和化油器等。 ( 4)冷却系统包括冷却风扇、引风罩等。有些背负式喷雾喷粉机在大风机后蜗壳上开冷却口,由引风罩引出冷却气流,就不再需要单独的冷却叶轮。 ( 5)润滑系统二冲程汽油机采用汽油与润滑油组合的混合油润滑与供油系统合用。四冲程汽油机润滑与供油分开,曲轴箱配有润滑油油面尺。 ( 6)配气系统四冲程汽油机由进、排气门,摇臂,推杆,挺杆及凸轮轴等组 成。二冲程汽油机没有进、排气门,而是在汽缸体上开有进气口、出气口和换气口,利用活塞上下运动来开启或关闭各气孔。 ( 7)启动系统有两种结构,一种是由启动绳和简单启动轮组成;另一种是回弹式启动结构,带有弹簧结合齿和防护罩等。 ( 8)点火系统包括磁电机、高压线、火花塞等。其中磁电机有两种:触点式带跳火架结构和无触点式电子点火线路。 汽油机工作时,完成进气、压缩、膨胀和排气一个工作循环,四冲程汽油机需要曲轴转两圈( 720),活塞上、下运动四次共四个行程;二冲程汽油机需要曲轴转一圈( 360),活塞上、下运动两次共 两个行程。 2.2 开槽机的传动机构 开槽机的传动机构可以选用带传动。 带传动是利用张紧在带轮上的柔性带进nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 4 页 行运动或动力传递的一种机械传动。根据传动原理的不同,有靠带与带轮间的摩擦力传动的摩擦型带传动,也有靠带与带轮上的齿相互啮合传动的同步带传动。2.2.1 带传动的类型 按带横截面的形状,带传动可分为平带传动、 V带传动、圆带传动和同步带传动等。其中平带传动、 V带传动、圆带传动为摩擦带传动,同步带传动为啮合带传动。 2.2.2 带传动的特点和应用 ( 1)传动带有弹性,能缓冲、吸振,传动较平稳,噪音小; ( 2)摩擦带传 动在过载时带在带轮上的打滑,可防止损坏其他零件,起安全保护作用。但不能保证准确的传动比。 ( 3)结构简单,制造成本低,适用于两轴中心距较大的传动。 ( 4)传动效率低,外廓尺寸大,对轴和轴承压力大,寿命短,不适合高温易燃场合。 带传动常用于中小功率的传动;摩擦带传动的工作速度一般在 5 25 m s之间,啮合带传动的工作速度可达 50m s;摩擦带传动的传动比一般不大于 7,啮合带传动的传动比可达 10。 2.3 平面连杆机构 开槽机通过选用连杆机构来控制切槽深度,连杆机构中的运动副一般为低副。其运动副元素为面接触,压 力较小,承载能力较大,润滑好,磨损小,加工制造容易,且连杆机构中的低副一般是几何封闭,对保证工作的可靠性有利。 2.3.1 铰链四杆机构的组成 铰链四杆机构是由转动副将各构件的头尾联接起的封闭四杆系统,并使其中一个构件固定而组成。被固定件称为机架,与机架直接铰接的两个构件称为连架杆,不直接与机架铰接的构件称为连杆。连架杆如果能作整圈运动就称为曲柄,否则就称为摇杆。 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 5 页 2.3.2 铰链四杆机构的类型 铰链四杆机构根据其两个连架杆的运动形式的不同,可以分为曲柄摇杆机构、双曲柄机构和双摇杆机构三种基本形式。 (1)曲柄摇杆机构。在铰链四杆机构中,如果有一个连架杆做循环的整周运动而另一连架杆作摇动,则该机构称为曲柄摇杆机构。 (2)双曲柄机构。在铰链四杆机构中,两个连架杆均能做整周的运动,则该机构称为双曲柄机构。 (3)双摇杆机构。两根连架杆均只能在不足一周的范围内运动的铰链四杆机构称为双摇杆机构。 1、铰链四杆机构中曲柄存在的条件 铰链四杆机构的三种基本类型的区别在于机构中是否存在曲柄,存在几个曲柄。机构中是否存在曲柄与各构件相对尺寸的大小以及哪个构件作机架有关。可以证明,铰链四杆机构中存在曲柄的条件为: 条件一:最 短杆与最长杆长度之和不大于其余两杆长度之和。 条件二:连架杆或机架中最少有一根是最短杆。 2、铰链四杆机构基本类型的判别准则 (1)满足条件一但不满足条件二的是双摇杆机构; (2)满足条件一而且以最短杆作机架的是双曲柄机构; (3)满足条件一而且最短杆为连架杆的是曲柄摇杆机构 ; (4)不满足条件一是双摇杆机构。 2.3.3 平面四杆机构的其它形式 1、曲柄滑块机构 在图 2-31a)所示的铰链四杆机构 ABCD 中,如果要求 C点运动轨迹的曲率半径较大甚至是 C 点作直线运动,则摇杆 CD 的长度就特别长,甚至是无穷大,这显 然给布置和制造带来困难或不可能。为此,在实际应用中只是根据需要制作一个导路, C点做成一个与连杆铰接的滑块并使之沿导路运动即可,不再专门做出 CD杆。这种含有移动副的四杆机构称为滑块四杆机构,当滑块运动的轨迹为曲线时称为曲线滑块机构,当滑块运动的轨迹为直线时称为直线滑块机构。直线nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 6 页 滑块机构可分为两种情况:如图 2-31b)所示为偏置曲柄滑块机构,导路与曲柄转动中心有一个偏距 e;当 e = 0即导路通过曲柄转动中心时,称为对心曲柄滑块机构,如图 2-31c)所示。由于对心曲柄滑块机构结构简单,受力情况好,故在实际生产中得 到广泛应用。因此,今后如果没有特别说明,所提的曲柄滑块机构即意指对心曲柄滑块机构。 应该指出,滑块的运动轨迹不仅局限于圆弧和直线,还可以是任意曲线,甚至可以是多种曲线的组合,这就远远超出了铰链四杆机构简单演化的范畴,也使曲柄滑块机构的应用更加灵活、广泛。 2、导杆机构 在对心曲柄滑块机构中,导路是固定不动的,如果将导路做成导杆 4铰接于A点,使之能够绕 A点转动,并使 AB杆固定,就变成了导杆机构,如图 2-32所示。当 AB BC 时,导杆能够作整周的回转,称旋转导杆机构,如图 2-32a)所示。当 AB BC时导杆 4只能作不足一周的回转,称摆动导杆机构,如图 2-32b)所示。 图 2-32 导杆机构 图 2-33 摇块机构及其应用 3、摇块机构和定块机构 图 2-31 曲柄滑块机构 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 7 页 在对心曲柄滑块机构中,将与滑块铰接的构件固定成机架,使滑块只能摇摆不能移动,就成为摇块机构,如图 2-33a)所示。摇块机构在液压与气压传动系统中得到广泛应用,如图 2-33b)所示为摇块机构在自卸货车上的应用,以车架为机架 AC,液压缸筒 3与车架铰接于 C点成摇块,主动件活塞及活塞杆 2可沿缸筒中心线 往复移动成导路,带动车箱 1绕 A点摆动实现卸料或复位。将对心曲柄滑块机构中的滑块固定为机架,就成了定块机构,如图 2-34a)所示。图 2-34b)为定块机构在手动唧筒上的应用,用手上下扳动主动件 1,使作为导路的活塞及活塞杆 4沿唧筒中心线往复移动,实现唧水或唧油。 图 2-34 定块机构及其应用 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献综述) 第 8 页 小结 在本次查找文献的过程中,我了解到了开槽机是通过特质刀片快速将不规则裂缝整理成均匀的凹槽,实现对沥青、水泥路面裂缝病害的处治功能,它的基本结构:动力机构,传动机构,四杆机构。为后面的设计确定了方向和理论基础。 参考 文献 1任殿阁,张佩勤 .机床设计指导 M.辽宁:科学技术出版社, 1991. 2何挺继 .水泥混凝土路面施工与施工机械 M.北京:人民交通出版社, 1999. 3何挺继,朱文天,邓世新 .筑路机械手册 M.北京:人民交通出版社, 1998. 4张世英 .筑路工程机械 M.北京:机械工业出版社, 1997. 5孙恒,陈作模,葛文杰 .机械原理 M.北京:高等教育出版社, 2006. 6曲继方,等 .机构创新原理 M.北京:科学出版社, 2001. 7刘吉善小型汽油机的发展动态 J.内燃 机工程, 1990,(2):32-38. 8陈佩珊,戌向新我国小型汽油机现状及发展 J小型内燃机,1994,(1):13-15. 9孟宪源 .现代机构手册 M.北京:机械工业出版社, 1994. 10弗尔梅 J.机构学教程 M.陈兆雄,译 .北京:高等教育出版社, 1990. 11濮良贵,纪名刚 .机械设计 M.北京:高等教育出版社, 2006.12吴宗泽,罗圣国 .机械设计课程设计手册 M.北京:高等教育出版社, 2006. 12德 S.弗罗尼斯 .设计学 :传动零件 .王汝霖,等译 .北京: 高等教育出版社,1988. 13Patton W.J.Mechanical Power Transmission.New Jersey:Printice-Hall,1980. nts 单位代码 0 2 学 号 080105655 分 类 号 TH6 密 级 秘密 毕 业设计 文献翻译 院(系)名称 工学院机械系 专业名称 机械设计制造及其自动化 学生姓名 金贺 指导教师 薛东彬 2012 年 3 月 10 日 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 1 页 针对不同的数控机床一个基于互联网的机床检查计划 Dong-ttoon Kim 情报和精密机械部门,韩国机械和材料研究所 ,大田 305 - 343,韩国 Sun-Ho Kim 机电工程专业本科工程 ,东义大学, Busan 614 - 714 釜山、韩国 Kwang-SIK KOH 电气工程和计算机科学学院,庆北国立大学,大邱广域市 702-701,韩国 摘要 本文提出了一个基于互联网的机床检查与数字控制机床 (CNC)技术。根据其体系结构的不同,数控机床分为两种类型:一种是封闭式控制结构( CAC),它是传统的数控机床;一种是开放式控制结构( OAC),这是最近推出的 PC-based 控制器。由于CAC 有一个封闭的架构,所以它依赖于数控机床供应商制定的规格。而因为这一点,它的应用程序很难在数控领域为用户所实现。近日,传统的数控机床已被基于 PC 的开放式数控机床所取代。然而,现在还有很多传统的数控机床在 OAC 配备不足的车间工作。对于 CAC 和 OAC 数控机床基于互 联网的检查,一个合适的系统环境是必要的。通过这项研究,对包括 CAC 和 OAC 在内的各种 CNC 在专业化生产系统进行全球化管理,对各种 CNC 基于互联网的检查设计一个合适的环境,并对 CAC 和 OAC检查方法作比较。这项研究成果可作为一个数控机床集成制造系统的全球监测和远程控制的基本模型。在本研究中定义的检查点分为两类:结构性点和操作点。前者包括轴承的振动,主轴单元的温度,和其他期刊管理点,而后者则包括油检查,夹具锁 /开锁,加工开 /关状态。 关键词: 基于 Internet 的检查方法,变式数控, CAC, 0AC 1 导言 电脑 和互联网的广泛使用,导致一个基于 Internet 的数控机床的控制和监测的全球化管理在专业化生产系统的需求不断增加。在过去,利用可编程逻辑控制器( PLC)的接触点,监测做为数控机床和制造系统外围设备的 I / O 信号。 但是,这个程序已经被限制到 CNC 内部信息的监测。它很难执行用户在数控领nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 2 页 域定义的程序,这个程序包括检查有关 CNC 的各种监测数据,外围设备和其他外部单位( Rober and Shin, 1995; Lee et.al.,2004)。而所需的用户自定义程序是数控机床监测与远程站点的通信应用程序模块。近日 ,基于 PC 的开放式结构数控机床取代了传统的数控机床,从而提供了一个方便的环境来实现用户定义的用于远程监视和控制的数控程序( Rober and Shin, 1995; Kwon et.al.,2000; Hong et.al.,2003)。然而,很多传统的数控机床在 OAC 配备不足的车间工作。为了做到对这种变式数控机床远程检查,应对每个 CAC 和 OAC 构建合适的环境。 现在,我们简要的概述下相关的研究。关于机床的开放式数控制造系统管理的研究,已经快速的实现了在柔性制造系统和自动配置( Wright, 1995)和动态重新 配置( Oldknow and Yellowley, 2001)的研究。一个开关函数发生器的研究解决了在开放式结构机床的维修机制( Kim et al., 2002)。 机床的远程控制和监测客户端 - 服务器环境也一直被研究( Oldknow and Yellowley, 2003)。这种关于远程服务的代表性例子是由 CNC 供应商开发的工厂窗口和远程系统( Kim et al., 2000;Kang and Kang, 1999)。然而,这些系统的特点是当地的域环境提高基本的技术支持。此外,这些研究还包括基于互联网的机床管理, CNC故障诊断的实现和基本的远程服务( Kim et al., 2003)。在柔性制造系统中基于 Web的监控也进行了研究( Jung et al., 2001)。此外,还研究了维护数控机床的公共交换电信电话网( PSTN)和数字 I / O 模块( Hyun et al., 1998)。 然而,这些研究都集中在 CAC 机除外的 OAC 机上,而研究的大多数的服务功能是通过电话线或外部网络(如 Internet)传输的监测数据。尽管是基于互联的应用程序,仍要安装一个开发商依赖的特殊的客户端,因为大多数情况下是基于客户 -服务器的配置。在 某些特殊情况下,一个额外的内核是必需的。此外,优越的数控厂商,如西门子的第三方支持通过互联网的网络服务。然而,在这情况下,非常困难的是服务的功能往往不适合车间修改功能。在国内,甚至有部分数控厂商无法服务一般商用的基于互联网的检查服务,如通过 lnternet 的监测。出现这种情况是因为大部分的运营商和数控厂商都集中在国内数控市场的稳定性和原创能力上面。也就是说,大部分的数控厂商都害怕数控机床因过载而崩溃或因故障造成额外软件安装或升级,所以他们支持远程服务功能。总之,虽然对 OAC 有一些研究,但是少有满意的设计,而 对 CAC 的研究更是非常缺乏。尤其是,基于互联网的检查与 CAC 和 OAC 的变种数控机床没有nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 3 页 得到充分的研究报告,由于不便开发环境和较差的软件可移植性。 本文调查申请的方法是基于互联网的检查技术,对 OAC 和 CAC 两个变式数控机床进行比较。通过这项研究建议通过基于 Internet 检查变式数控机床的有效计划。首先,远程检查和控制与 CAC 的机床和零部件相关的数字信号,通过使用 I / O 的嵌入式模块介绍网页;其次,本文认为模拟和数字远程检查 OAC 的机器通过实施相关的信号用户定义的应用程序能够接口与外部服务器的数控域,并通过 数据采集单元( DAU),能够获得与连接的数据机及周边设备的联系点。 CAC 有一个封闭的架构,它是依赖数控协力厂商规范。由于这一点,就已经很困难,为用户实施在数控应用程序。因此,一个特殊的,额外的模块需要基于互联网的应用程序(塞纳科技, 2002 年)。对于这一点,一个网络的 I / O 嵌入式模块适用于本研究基于互联网的检查。模块直接连接到 TCP/ IP 网络与远程通信网站。为了获得监测数据数控机床,模块的 I / O 信号在数控被分配到 PLC 的 I / O 信号。另一方面, OAC有一个基于 PC 的开放式架构,运作独立于数控供 应商的规范并没有额外的模块是必要的,用于连接远程站点。正因为如此,一个简单的 DAU,这是不直接连接到 OAC的主要电路板,而不是直接影响到数控稳定,用于信号传感和数据通过 RS232/422 行收购无需额外通信设备模块。基于 Internet 的远程机器检查与 OAC,用户定义的守护进程的工具通信和应用程序 Web 服务的形式实现 OAC 和内部功能内外部服务器。互联网通信之间进行数控领域的守护程序外部服务器和网络脚本程序。nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 4 页 2 基于 Internet 检查 OAC 的方法 在 OAC 的情况,不需要网络支持附加设备模块, OAC 有一个方便 的结构,可以实现网络应用程序。检查和获得机床 I / O 信号的数据,只需要信号处理板或外部的DAU 数据采集。由于大多数 OAC 是基于单板计算机上的 DAU 一个紧凑的结构,比板型( Advantech, 2002)更有效可以简单地连接 I / O 信号。试图通过监测加工状态,应用程序通过 DAU 零部件温度和振动的检查方法,可以通知检查时间和零部件的更换时间。通过这个应用,数控机床及周边设备的模拟和数字接触点监测使用的 DAU。在实验中,使用外部的 I / O 的 DAU 模块,以减少硬件设备的大小,并尽量减少负荷。基于 Internet 的检查 OAC 机床配置使用的 DAU 如图 1RS485 通讯内部通过 RS232/485转换规范。 0V 至 1.5V 的范围内分配一个采样周期为每秒 10 次,以获取模拟传输值。为获取轴承的振动和主轴温度的实验,传输的模拟值在 OAC 和 DAU 之间的通信协议实时监控,如图 2 所示 Subsequently,也进行检查开 /关状态的石油和钳的基本实验,如图 3 所示功能的应用程序代码,实现在 OAC 数控域的内部功能。 基于 Internet 的检查应用,通讯发达的守护程序在数控领域实施,在外部服务器由 Web 服务的 Web scr.ipt 方案实施,使用 vbscrip, JavaScript 和活动服务器页面( ASP),如图 4 守护程序之间的网络通信可以在数控域和外部 Web 脚本程序。因此,多个客户端可以监控检查的数据和机器的状态,通过收购数字和模拟数据传输从外部数据库的OAC。数控通信服务程序采用标准的开放式数据库连接( ODBC)和数据处理,利用结构化查询语言( SQL)查询。通过这个过程,检查数据传输相关的表中的信息构建在数据库表中。在互联网环境下的远程检查,实现了通过设计的应用程序,如图 5 所示结果表明,这种检查方法是有利的,在其方便的开发环境在软件方面,可以很 容易地实现用户定义的应用程序。 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 5 页 图 1 基于互联网的检查 OAC 的机器配置使用的 DAU 图 2 通信协议之间的 OAC 的 DAU 模nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 6 页 图 3 模拟输入( 0-1.5V 的范围)的收购和数字输入( 8 位直接投资) 图 4 OAC 和应用程序之间的接口网站 SEVER nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 7 页 图 5 检查 OAC 的机器所使用的 DAU 和应用程序 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 8 页 3 基于 Internet 的检查计划和变式数控机床的例子 基于互联网的检查的计划变型数控机床的建议图 6CAC 机区旨在检查通过下载脚本代码的数字数据和嵌入式设备服务器的 I / O 接口机制。在 OAC 机区检查 所使用的DAU 和应用程序,如数据采集模块,通信守护进程模块,和一个 web 脚本模块的模拟数据和数字数据。基于互联网的变种数控机床的远程检查,通过拟议的计划表见图7 在 CAC 的机床的情况下,一个 Java applet 被编码和下载,以检查机床的 I / O 数据和通过网络浏览器向客户提供检查结果。在 I / O 地址的 Java applet 代码和真正的 I / O 点的机床之间分配,监视和控制远程站点。展示的内容是对监测结果 I / O 的接触点与当前加工 /关状态。 CAC 的机床运作周期的启动按钮正在网页浏览器上。 在 OAC 机 床的情况下,收购的 DAU 监测数据传送到在远程站点,外部服务器和通信守护进程服务。它通过网络浏览器激活油传感器,主轴温度是 0.0007(这是从 0至 1.5 V 范围内的模拟值)。 结果表明,在前一种情况下, CAC 是有利的,它可以很容易地利用网络功能的嵌入式设备,在硬件实现基于 lnternet 的检查系统。然而,用户定义的应用程序和下载数据的最大尺寸被限制在 512 字节;后者的情况下,在其方便的开发环境,可以方便地实现在数控领域的许多不同的应用程序,无需额外设备的优点。然而,用户定义的应用程序编程工作需要比在前者的情况 下实施通信和网络服务。 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 9 页 图 6 基于互联网的检查环境变异数控机床 图 7 例如基于互联网的远程检查变种数控机床 nts 黄河科技学院毕业设计(文献翻译) 第 10 页 4 结论 本文提出了一种新的研究基于 Internet 检查传统的 CAC 和最近推广的 OAC 两种变式数控机床。为了实现基于互联网高效的检查 CAC 机,使用信号检测方法,通过网络 I / O 嵌入式设备模块,可以支持互联网应用环境,因为在 CAC 的环境执行用户定义的应用程序,是依赖于数控厂商规范了的数控领域。 为了实现基于互联网检查 OAC 机床,数字和模拟信号的检查方法,它不需要额外的网络 I / O 的 互联网应用的嵌入式设备,有人建议,因为数控域执行用户定义的应用程序很容易因方便 OAC 的环境。这种方法只需利用的 DAU 取得的 I / O 硬件方面的数据和采集到的数据传送到外部服务器通过在远程站点上的网页浏览器的远程检查。 随后,对 CAC 和 OAC 机的检查方法进行了比较。通过这项研究,为数控机床与数控变种的 CAC 和 OAC 在制造系统,基于互联网的变型数控机床的检查,被设计为一体的综合经营的一个合适的环境,如建筑的全球管理。这项研究的结果可能是一个全球监测和远程控制在变种数控机床集成制造系统的基本模型。 在今后的工作中 应解决以下问题:首先,研究人员应该调查优越的远程检查环境的设计和实现,可以在嵌入式设备利用足够的上下载的代码;其次,还需要进一步研究,可以更简单地对集成和经营变式数控机床的标准化和优化应用程序进行开发。 感谢 感谢工业改造技术项目(商务部,工业和能源)提供的财政支持。 ntsJournal of Mechanical Science and Technology, Vol. 19, No. 1, pp. 97-105, 2005 97 A Scheme for an Internet-based Checking Method of Machine-Tools with Variant CNC Architecture Dong-ttoon Kim* Department of Intelligence and Precision Machines, Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials, Daejeon 305-343, Korea Sun-Ho Kim Mechatronics Engineering Major, College of Engineering, Dong-Eui University, Busan 614-714, Korea Kwang-Sik Koh School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea This paper proposes an Internet-based checking technique for machine-tools with variant Computerized Numerical Controller (CNC). According to its architecture, CNC is classified into one of two types : Closed Architecture Controller (CAC), which is the conventional CNC, or Open Architecture Controller (OAC), which is a recently introduced PC-based controller. Since CAC has a closed architecture, it is dependent on CNC vender specification. Because of this, it has been very difficult for users to implement application programs in the CNC domain. Recently, the conventional CNC of machine-tools has been replaced by a PC-based open architecture CNC. However, now many conventional CAC machines are being operated together with OAC machines in inadequately equipped shop floors. For Internet-based checking for variant CNC machines with CAC and OAC, a suitable systematic environment is necessary. Through this research, for the global management of variant CNC machines both a CAC and an OAC in the manufacturing system, a suitable environment for Internet-based checking of variant CNC machines was designed, and the checking methods for CAC and OAC machines were compared. The results of this research may serve as a base model for global monitoring and remote control in an integrated manufacturing system with variant CNC machines. Checking points defined in this research are classified into two categories: structured point and opera- tional point. The former includes the vibration of bearing, temperature of spindle unit, and other points of periodical management, while the latter includes oil checking, clamp locking/ unlocking, and machining on/off status. Key Words : Internet-Based Checking Method, Variant CNC, CAC, 0AC I. Introduction Widespread use of computers and the Internet * Corresponding Author, E-mail : kdh680 kimm.re.kr TEL : -t-82-42-868-7148; FAX : -t-82-42-868-7150 9 Department of Intelligence and Precision Machines, Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials, Daejeon 305-343, Korea 9 (Manuscript Received June 11, 2004; Revised October 25, 2004) have led to a continuously increasing demand for Internet-based control and monitoring of CNC machines for distributed global management in manufacturing systems. In the past, the contact points of Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) were utilized for the monitoring of I/O signals associated with CNC machines and peripheral equipment in manufacturing systems. However, this solution has been limited to the monitoring of CNC internal information. It has Copyright (C) 2005 NuriMedia Co., Ltd. nts98 Dong-Hoon Kim, Sun-Ho Kim and Kwang-Sik Koh been difficult to check various monitoring data regarding the CNC, peripheral equipment, and other external units by implementing user-defin- ed programs to the CNC domain (Rober and Shin, 1995 ; Lee et. al., 2004). The required user- defined programs are application modules for the monitoring of CNC machines and for com- munication with a remote site. Recently, a conve- nient environment able to implement user-defin- ed programs to a CNC domain for remote moni- toring and control has been provided, since the conventional CNC of machine-tools has been replaced by a PC-based open architecture CNC (Rober and Shin, 1995 ; Kwon et. al., 2000 ; Hong et. al., 2003). However, many conventional CAC machines are now being operated in inadequately equipped shop floors. In order to do a remote check on such variant CNC machines, a suitable environment for each case of the CAC and the OAC should be constructed. We will now briefly outline the related re- search. Regarding research on the management of machine-tools with open architecture CNC in manufacturing systems, there have been studies on rapid part realization in flexible factory sys- tems (Wright, 1995) and on automatic configura- tion and dynamic reconfiguration (Oldknow and Yellowley, 2001). A study on switching function generators addressed the maintenance mechanism of machine-tools with open architecture CNC (Kim et al., 2002). Remote control and monitoring of machine tools by client-server environments has also been investigated (Oldknow and Yellowley, 2001; Kim et al., 2003). The representative examples for such remote services are factory windows and remote systems that are developed by a com- mercial CNC vendor (Kim et al., 2000 ; Kang and Kang, 1999). However, these systems are char- acterized by basic technical support in local domain environments. Besides of this, as for re- search on Internet-based management of mac- hine-tools, CNC-implemented fault diagnosis and basic remote services were reported (Kim et al., 2003). Web-based monitoring has been stu- died in a flexible manufacturing system (Jung et al., 2001). Furthermore, Public Switched Tele- Copyright (C) 2005 NuriMedia Co., Ltd. phone Network (PSTN) and digital I/O modules were utilized for research on the maintenance of CNC machines (Hyun et al., 1998). However, these researches have focused on only OAC machines except CAC machines and the most service function is to transmit moni- toring data via telephone line or external net- work such as Internet. Although in the case of Internet-based application, a special client-ter- minal program, which is dependent of developer, has to be installed because the most cases are based on client-server configuration. In some special cases, an additional kernel is optionally required. Besides, the third-party of superior CNC vendor such as Siemens supports partially the web services via Internet. However, in this case, the service functions are not often suitable to the shop-floor and the modification of the functions is very difficult. In domestic case, even representative CNC vendor can not service gen- erally and commercially the Internet-based chec- king services such as conditions monitoring via lnternet. The cause of such actual circumstance mentioned above is because most operators and CNC vendors have focused on the stability and original ability of CNC in domestic CNC market. That is, most CNC vendors are afraid of the breakdown of CNC machine-tools due to over- load and faults resulting from additional soft- ware installation or upgrade for the purpose of supporting the functions such as remote services. In short, although there are some researches av- ailable for machines with OAC, satisfied applica- tion cases are rare yet and the studies on machines with CAC have been very deficient. Especially, research on Internet-based checking for variant CNC machines with a CAC and an OAC has not been sufficiently reported due to the inconvenient development environment and inferior software- portability. This paper investigates methods for applying Internet-based checking techniques to variant CNC machines with OAC and CAC, and the two types of CNC are compared. And an efficient scheme for Internet-based checking for variant CNC machines is suggested through this study. First, remote checking and control of the digital ntsA Scheme for an lnternet-based Checking Method of Machine-Tools with Variant CNC Architecture 99 signals associated with CAC machines and com- ponent parts by using a web I/O embedded mo- dule are introduced. Second, this paper consi- ders the remote checking of analog and digital signals associated with OAC machines by imple- menting user-defined application programs able to interface with an external server to the CNC domain, and by using a Data Acquisition Unit (DAU) able to acquire data connected with the contact points of machines and peripheral equi- pments. CAC has a closed architecture which is depen- dent on CNC vender specification. Because of this, it has been very difficult for users to imple- ment an application program in CNC. Therefore, a special, additional module is required for Internet-based application (Sena Technologies, 2002). For this, a web I/O embedded module was applied for Internet-based checking in this re- search. The module is directly attached to the TCP/IP network for communication with a re- mote site. In order to obtain the monitoring data of CNC machines, the I/O signals of the module were assigned to PLC I/O signals within CNC. On the other hand, OAC has a PC-based open architecture that operates independent of CNC vendor specification and no additional module is necessary for connection with a remote site. Because of this, a simple DAU, which is not directly attached to OAC main-board and not directly affects to CNC stability, is used for signal sensing and data acquisition via RS232/422 line without additional communication device mo- dule. For Internet-based remote checking of ma- chine-tools with OAC, a user-defined daemon for communication and application programs for web services were implemented in the form of internal function within OAC and an external server. Internet communication is performed be- tween the daemon program of the CNC domain and web script programs of the external server. 2. Structure of Variant CNC Machines and Remote Checking Directions As mentioned above, the implementation of a Copyright (C) 2005 NuriMedia Co., Ltd. user-defined application program is much more difficult in the CAC than in the OAC due to the inconvenient development environment of the CAC. Because the CAC is fully dependent on the CNC vendor, as shown in Fig. 1 (a), the CAC cannot support the application of user-functions that can connect with the network and remotely check CNC machines in the CNC domain. How- ever, as shown in Fig. 1 (b), it is convenient for users to implement the application programs for remote checking in the OAC domain because the OAC has an open architecture based on a PC. For Internet-based remote checking of these two CNC machines that are operated together in a manufacturing system, a suitable system environ- ment must be constructed according to the struc- ture characters of the variant CNC. The conven- tional CAC with closed architecture can effi- ciently use the network-supported unit with em- bedded web server functions because connecting the I/O signals of the applied unit with the I/O signals of CNC machines is possible. This method has an relatively simple system architecture for users, but its fatal flaw is that it cannot manage multiple CNC machines simultaneously with a single server and web script program ; this meth- od, using web-server functions embedded in the device, requires that an individual Internet Pro- tocol (IP) address be associated with each ma- chine. For the recently popularized OAC with a (a) CNC with closed architecture controller (b) CNC with open architecture controller Fig. 1 Structure of variant CNC machines nts100 Dong-Hoon Kim, Sun-Ho Kim and Kwang-Sik Koh PC-based open architecture environment, instead of using network-supported units that require additional unique IP addresses, a suitable method is as follows. First, a DAU is utilized in order to acquire I/O data. Then the application program for data acquisition is implemented in order to check I/O contact signals through the DAU, and the interface daemon program, that can transmit the acquired data from a CNC domain to an external server, is implemented in the CNC do- main. A particularly outstanding merit of this system is that a lot of CNC machines can be monitored and managed simultaneously without an additional device with embedded web-server functions. This method also has good expansi- bility. 3. Definition of Checking Points As shown in Table 1, the checking points defined in this research are classified into two categories : structured point and operational point. The former includes the vibration of bear- ing, and the temperature of the spindle unit and other specific units, while the latter includes oil checking, clamp locking/unlocking, and other digital checking points associated with machine operations. Table 1 Definition of checking point Structured Conditions Operational Conditions Vibration of bearings Machining On Temperature of spindle Machining Off Vibration of bearing2 Fault (No Ready) Temperature of spindle2 Oil checking Vibration of bearing3 Clamp lock/unlock Temperature of spindle3 Sub unit on/off 4. Internet-Based Checking Method for CAC Machines This section describes the application of an Internet-based checking method for CAC mac- Fig. 2 hines. In remote monitoring of checked results Copyright (C) 2005 NuriMedia Co., Ltd. and related information with CAC machines, the application program implementation and the program running environment in the CNC do- main are more limited than in an OAC environ- ment that can easily implement software func- tions. Because an additional device module is necessary, we utilized the I/O module with em- bedded minimum operating system and web ser- ver functions, as shown in Fig. 2. By applying this module, the control and monitoring of CNC machines were remotely performed in the experi- ment. The applied device module supports a total of 32 I/O contact points in order to interface with external devices. The contact points were connected with the PLC I/O signals of the CAC machine. Through these points, the machine sta- tus such as cycle start, stop, emergency stop, and machining on/off status can actually be moni- tored in a web environment. The procedure for the application test is as follows. The icons associated with the I/O device module are first designed in default html source by using the supplied device utility, and then the icons properties are assigned to specific I/O addresses. Next, network-supported java class is inserted in default html source and the source codes are compiled by the utility compiler. After that, coded web script files are transferred to the specific file index format so that they can be interpreted by the device module engine (Sena CAC Machine .q D PLC/PMC Z 176 I,. N ooo ooo _ Digital tlO Connection (Digital I/0 Interface Method) .: l Browser Ethernet cable I Hub/SwitCh t Internet-based checking configuration using embedded web I/O device for CAC machine ntsA Scheme for an Internet-based Checking Method of Machine-Tools with Variant CNC Architecture 101 Technologies, 2002). The transferred file, that is in the form of a specific format, is a single image file format that is downloaded to flash memory, as shown in Fig. 3. In order to assign the phy- sical I/O device addresses in application source codes, the real I/O addresses are mapped with the icon properties in web script sources such as html, vbscript, and javascript, as shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 5 shows that the status of the CAC ma- chine is now checked as machining-on when the cycle-start button is selected through a web browser. And through additional analog checking experiment for structured conditions, bearing vi- bration and spindle temperature were monitored in real time. The remote checking model of the CAC machine and its implementation method are relatively simple and convenient, but a database and large-scale script files cannot be loaded. In I User-defined application modules I Cnneetor to Interact Power Supply 16po Sensor nput Conttc Point Fig. 3 Interface between embedded web I/O device and application program detail, a maximum 512 Kbytes application script program can be downloaded to the web I/O embedded device module. However, this method can be very efficient in applications as it uses an I/O board independent of other systems. Here, for remote checking, web script was coded by using java applet and was downloaded to the web I/O embedded device module. For interfacing with the I/O of the CNC machine, I/O contact points were directly connected with each other between the embedded web I/O device and the machine I/ O signals. Test results confirmed that the applica- tion system environment can be easily designed by using this checking method. Table 2 Hardware specification of used web I/O device Item Content CPU 8-bit Microprocessor 512 KB Flesh Memory Memory (User Web File/Parameter App.) Network 10-base T Ethernet (IEEE802.3) Connection External 16 point Digital Input, Connection 16 point Digital Output Internet Protocol HTTP/TCP/UDP/IP/Ethernet Board (Vendor) Dependency, Utility software IP Setting/Web Page Uploading Icons and html implementation by using device
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号