双盖注塑模具设计【优秀含10张CAD图纸+塑料模具全套毕业设计】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:479262
类型:共享资源
大小:1.96MB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2015-10-07
上传人:小***
认证信息
个人认证
林**(实名认证)
福建
IP属地:福建
45
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
注塑
模具设计
优秀
优良
10
cad
图纸
塑料模具
全套
毕业设计
- 资源描述:
-
!【详情如下】【注塑塑料模具课题】CAD图纸+word设计说明书.doc[11000字,32页]【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ97666224】.bat
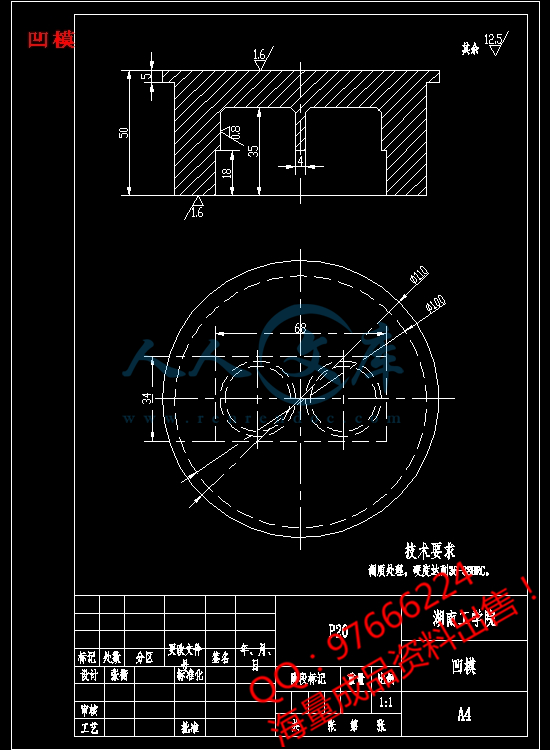
凹模.dwg
型芯.dwg
型芯固定板.dwg
塑件图.dwg
定模座板.dwg
定模板.dwg
推件板.dwg
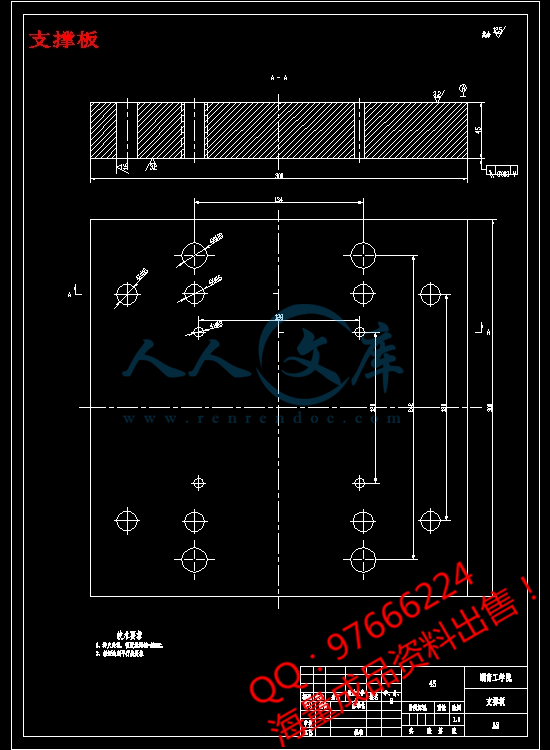
支撑板.dwg
浇口套.dwg
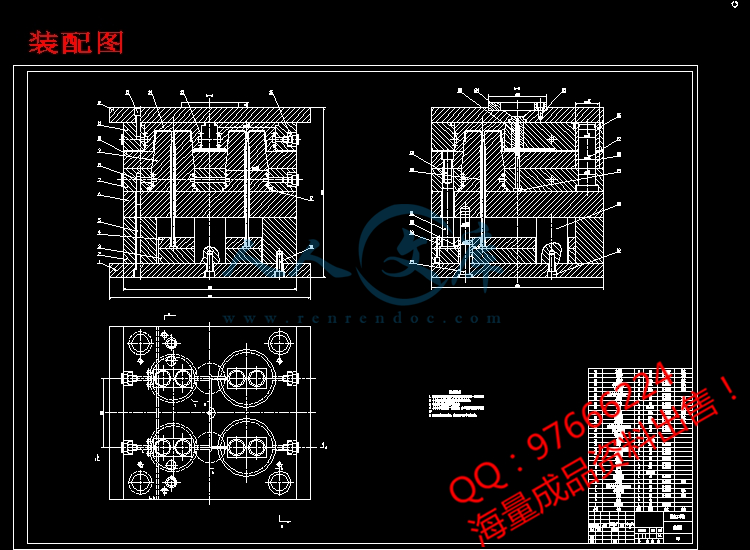
装配图.dwg
设计任务书.doc
设计说明书.doc[11000字,32页]
开题报告和中期检查表.doc
外文翻译
摘 要
本课题主要是针对塑料盖的模具设计,通过对塑件进行工艺的分析和比较,最终设计出一副注塑模。该课题从产品结构工艺性,具体模具结构出发,对模具的浇注系统、模具成型部分的结构、顶出系统、冷却系统、注塑机的选择及有关参数的校核都有详细的设计,同时并简单的编制了模具的加工工艺。通过整个设计过程表明该模具能够达到此塑件所要求的加工工艺。根据题目设计的主要任务是塑料盖注塑模具的设计。也就是设计一副注塑模具来生产盒盖塑件产品,以实现自动化提高产量。
关键词:塑料盖;注塑模;模具结构;浇注系统;注塑机
ABSTRACT
This topic mainly aimed at the mold design of plastic lid. Through the analysis and comparison of the plastic product , the plastic injection mold was designed. This topic came from the technology capability of product, the structure of the mold embarks, the gating system, the injection molding system and the related parameter examination, the mold took shape the partial structures, the against system, the cooling system ,the injection molding machine all had the detailed design, at the same time , the processing craft of the mold were simply established. Through the entire process of the design indicated this mold can achieve the processing craft which the plastic lid requested.
Key words:plastic lid;plastic injection mold;the structure of the mold embarks;gating systerm; injection molding machine
目 录
前言1
1 塑件成型的工艺性分析4
1.1塑件的分析4
1.2 PP的性能分析4
1.3聚丙烯的成型工艺4
2 注射机的型号和规格选择及校核6
2.1 注射机的选用6
2.2 注射压力的校核7
2.3 锁模力的校核7
3 分型面的选择8
3.1 分型面的形式8
3.2 分型面的选择原则8
3.3 水平分型面的选择8
4 型腔数目的决定及排布9
4.1 型腔数目的确定:9
4.2 多型腔的排列:9
4.3 模具结构的初步确定9
5 浇注系统的设计10
5.1主流道设计:10
5.2分流道的设计11
5.3浇口的设计:13
5.4 校核主流道的剪切速率13
5.5冷料穴的设计13
6 成型零件的工作尺寸计算14
6.1 凹模的结构形式14
6.2 凸模的结构设计14
6.3 成型零件的工作尺寸计算15
6.3.1 凹模径向尺寸计算15
6.3.2 凹模深度尺寸的计算16
6.3.3 型芯径向尺寸计算16
6.3.4 型芯高度尺寸的计算17
6.3.5型腔的壁厚和底板厚度的计算17
7 模架的确定18
7.1各模板尺寸的确定18
8 导柱导向机构的设计19
9 脱模推出机构的设计20
9.1 脱模力的计算20
9.2 推出方式的确定20
9.3 脱模机构的设计原则20
10 温度调节系统的设计21
10.1 冷却系统设计21
10.2 冷却时间的确定21
10.3 冷却系统设计原则21
10.4 冷却系统的计算22
11模具安装23
设计总结24
参考文献25
致 谢26








- 内容简介:
-
Optimization of Gate, Runner and Sprue in Two-Plate Family Plastic Injection Mould M.A. Amran*, M. Hadzley, S. Amri, R. Izamshah, A. Hassan, S. Samsi, and K. Shahir1Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering, Universiti Teknikal Malaysia (UTeM), Locked Bag 1200, Hang Tuah Jaya, Ayer Keroh, Melaka, Malaysia *Email: mohdamran.my Abstract. This paper describes the optimization size of gate, runner and sprue in two-plate family plastic injection mould. An Electronic Cash Register (ECR) plastic product was used in this study, which there are three components in electronic cast register plastic product consist of top casing, bottom casing and paper holder. The objectives of this paper are to find out the optimum size of gate, runner and sprue, to locate the optimum layout of cavities and to recognize the defect problems due to the wrong size of gate, runner and sprue. Three types of software were used in this study, which Unigraphics software as CAD tool was used to design 3D modeling, Rhinoceros software as post processing tool was used to design gate, runner and sprue and Moldex software as simulation tool was used to analyze the plastic flow. As result, some modifications were made on size of feeding system and location of cavity to eliminate the short- shot, over filling and welding line problems in two-plate family plastic injection mould. Keywords: Computer Modeling; Flow Simulation; Optimization PACS: 07.05Tp 1. INTRODUCTION The plastic injection generally has three phase processes comprising filling, packing and cooling phases. The introduction of simulation software has made a significant impact in the mould making industry with the increasing use of computers in design engineering, the amount of commercially available software on the market has also increased 1. The ECR plastic product uses same material and colour, however different size of part. Each part has it own mould but on this research, all the parts used family mould. The difficult stage to design family mould is to decide the mould layout, injection location, size of gate, runner, sprue and location of water holes 2, 6, 7. To investigate the flow behaviour the Moldex software as simulation software was used to analyze the plastic flow. 2. METHODOLOGY This study started from design 3D modeling of ECR product using Unigraphic software and then the files were transferred into Rhinoceros software for post processing. In Rhinoceros software the feeding system such as gates, runners, sprues, 309ntswaterholes and mould base were designed. Finally, Moldex software is used by importing file from Rhinoceros software. Plastic materials, processing conditions were decided before filling, packing, cooling and warpage analysis. If results do not satisfy, the modification will be done again as shown in Figure 1. EndInterperet data &make conclusionYESRun analysisSelect materialSet processing conditionTransfer file to Moldex softwareDesign water holes systemDesign rectangular edge gate Design circular cross section runner Design direct sprueDesign circular layoutNOTransfer file to Rhinoceros softwareMeshing part surfaceDesign part in 3D using UnigraphicStartFIGURE 1. Methodology of analysis. 3. DESIGN OF TWO PLATE MOULD All ECR files consist of top casing, bottom casing and paper holder which they were exported from Unigraphic software to the Rhinoceros software through step one by one. The files were saved under DXF extension which it can be read by Rhinoceros software. Initially, the top casing file was opened in Rhinoceros software which it was converted from solid modeling into mesh modeling as shown in Figure 2(a). Further, Figure 2(b) shows the early stage of imported file of bottom casing from Unigraphic software to Rhinoceros software. The refine mesh of bottom casing has been made until the fine mesh of surface is achieved. The cavity surface was remained after core side had been deleted by removing the mesh. The same method was done for paper holder as shown in Figure 2(c). 310nts (a) Top Casing (b) Bottom Casing (c) Paper Holder FIGURE 2. Mesh modeling of ECR. 3.1 Rectangle Edge Gate Two sizes of rectangular edge gate need to decide which are depth and width. The depth of these parts are calculated using formula h = nt, where h is depth of gate (mm), t is wall section thickness (mm) and n is material constant 3. Calculation from this formula the depth of top casing and bottom gate are 1.2 mm and paper holder is 1.8 mm. The width of edge gate is derived from equation 1 4. W= n x A / 30 (1) Where, W is gate width (mm); A is surface area of cavity (mm2) and n is material constant. From calculation surface area of top casing is 84,648 mm2,the width is 5.8 mm. Further calculation, bottom casing width is 5.9 mm and paper holder is 1.27 mm. 3.2 Circular Runner Diameter runner was calculated by taking the weight of part from volume multiply density and distance part from centre of mould as equation 2 4. D = W x L / 30 (2) Where, D is runner diameter, W is part weight and L is distance part to centre mould. Volume of top casing was taken from Rhinoceros software is 78,202 mm3and the weight is 0.08 kg so the diameter of runner is 6.5 mm. Further calculation, the diameter of bottom casing is 6.7 mm and paper holder is 1.5 mm. 3.3 Sprue The sprue size was decided by taking the thickness cavity plate mouldbase and given angle one degree from diameter 7 mm. Initial cold slug well is 7 mm and base cold slug well is 10 mm. Figure 3 shows the location of top casing, bottom casing and paper holder together with feeding system. FIGURE 3. Layout of two-plate mould. 311nts4. FILLING ANALYSIS OF TWO PLATE MOULD Result from filling analysis shows that the total filling period is 1.041 seconds. At the stage, 100% there were two results where the top casing was short shot and the plastic cannot flow to the impression of paper holder as shown in Figure 4. FIGURE 4. Filling process The top casing was redesigned because of the meeting area of flow front situated at side body, as result a welding line was developed on that area as shown in Figure 5. Welding line is the result of a flow front, which easily breaks up into two separate parts. When the two fronts meet, they try to welding back together again so as result form a single front line which it can be easily broken down 5. FIGURE 5. Welding line at top casing 4.1 Modification on Two-Plate Mould Modification was done on gate of bottom casing by decreasing 25% from 5.9 mm to 4.3 mm and runner from 6.7 mm to 5 mm due to over filling. Location of paper holder was moved from 50 mm from center of mould to 25 mm and increase runner size by 25%. A set of groove was added on surface of top casing to ensure the plastic flow toward corner of top casing as shown in Figure 6. FIGURE 6. Modification of Two-Plate mould. 312nts4.2 Filling process after Modification Result from filling analysis after modification shows the melt of plastic of three components were balance on each other. The total filling melt front time is 7.804x10-1seconds. The welding line has been eliminated on the centre side body of top casing and as result melt plastic flows towards on the corner as shown in Figure 7. FIGURE 7. Filling process after modification 5. DISCUSSION The size of runner of paper holder was increased and shifted to eliminate the unfilling. Gate and runner of bottom casing were decreased due to the over filling. Top casing was redesigned by adding a set of groove on the top surface of top casing to eliminate the welding line. As the result the welding line on centre side body of top casing was eliminated. From results it was found that the size of gate and runner in two-plate mould for paper holder increased by 25% due to the short shot problem and gate and runner for bottom casing reduced by 25% due to the over filling. 6. CONCLUSION This study was success on analyzing the flow of plastic materials in two-plate mould. The modifications was done on layout of cavities and feeding system as result improved the quality of the product. Furthermore, the defects of plastic product on short shot, over filling and welding line were eliminated before the actual mould is fabricated. REFERENCES 1. S.S.S. Imehezri., S.M. Sapuan, S. Sulaiman, Journal Material and Design, volume 26, pp. 157 166, 2005. 2. L.T. Manzione, Applications of Computer Aided Engineering in Injection Molding, Hanser, New York, 1987. 3. R.G.W. Pye, Injection Moulding Design, Longman Scientific & Technical, New York, 1989. 4. G. Monges & P. Mohren, How to Make Injection Molds, Hanser Publishers, New York, 1993. 5. M.B. Douglas, Plastics Injection Moulding- Manufacturing Process Fundamentals. Society of Manufacturing Engineer, Michigan, 1996. 6. C.T. Wong, S. Sulaiman , N. Ismail, A.M.S. Hamouda, Procedings of Second World Engineering Congress, Sarawak, Malaysia,. pp. 193-198, 2002. 7. M. Khairol, Master Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 2001. 313ntsCopyright of AIP Conference Proceedings is the property of American Institute of Physics and its content maynot be copied or emailed to multiple sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holders express writtenpermission. However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use.nts 两板式塑料注塑模的浇口,分 流 道 和主 流道的优化 摘要:本文介绍了两板式塑料注塑模的浇口, 分流道和主 流道的优化尺寸大小。 电子收款机( ECR)的塑料制品被用于这项研究中,其中有三个电子元器件铸塑料制品包括登记套管顶部,底部套管和纸架。本文的主要目的是找出 浇口,主流道和分流道的最佳尺寸和最佳布局,找出导致浇口,主流道和分流道尺寸不合适的原因。这项研究中使用了三种类型的软件 , 如 CAD 工具软件 UG 被用来设计 3D 建模,犀牛软件作为标杆处理工具被用来设计浇口、分流道、主 流道和Moldex 软件作为仿真工具被用来分析塑性 流动。因此,修正了型腔进给系统的位置和尺寸大小,以消除短杆,过充和两板系列注塑模具焊缝问题。 关键词: 计算机建模;仿真流动;优化 1简介 通常的注塑过程 包括三个阶段 :注射 ,合模 和冷却阶段。 本文 介绍了 随着 计算机日益广泛的应用在设计工程 , 仿真软件 在 模具制造行业的重大影响 ,而 大量的商用软件市场也增加了 1。 ECR 塑料产品采用相同的材质和色彩 ,然而 各部分尺寸大小不同 。每个部分都有它自己的模具 , 但这个研究 ,所有的 部分都用了这种系列的 模具。设计模具 的困难 阶段是决定 这种系列 注射模具的 浇口 、 分 流道 、主 流道的 布局、位置、 大小与水孔的位置 2,6,7。 为了 探讨了流动行为 , Moldex软件仿真 软件 用于分析塑性流动。 2 方法 本研究首先从设计产品三维造型的 ECR 使用 UG 软件,然后在文件被转移到犀牛软件后处理。在 犀牛软件 的进给系统如浇口 , 分 流道 , 主 流道 , 水口和模具设计进行了设计 。最后, Moldex 软件 从犀牛软件中 使用 进口文件。塑料 原料,工艺条件 决定前要进行注射 , 合模 ,冷却和 热曲线 分析。如果结果不符合, 必须修改后 再 进 行,如图 1 所示。 nts 1 图 1 方法分析 3 设计 双板模具 所有的 ECR 的文件包括顶级套管,套管和底纸架 ,他们 分别一步一步出自UG 软件犀牛软件。该文件被保存在 DXF 扩展 文件 , 它可以通过 犀牛软件 来读取 。起初,顶套管中打开文件,它是犀牛软件 从实体模型转换成网状模型,如图 2( a)。此外,图 2( b)显示了从 UG 进口的早期阶段底部外壳文件软件犀牛软件。外壳的底部 表面细网的实现 后 取得了细化网格。腔表面后仍然 存在,在 核心 方已被删除从移开 的网格。同样的方法 用于纸架 ,如图 2( c) 所示 。 图 2 ECR 的网建模 nts 3.1 矩形边缘浇口 矩形边缘浇口 需要确定的 尺寸是深度和宽度。该部件深度计算公式为 h =nt,其中 h是门深入(毫米) , t 为墙截面厚度(毫米), n 为材料常数 3。从 这个公式 可以得出的浇口 套管深度 为 1.2 毫米和纸架深度为 1.8 毫米。 边缘浇口的宽度 从公式 1 4 推导 。 W= n x A / 30 (1) 其中, W 为浇口 宽度(毫米), 是表面面积腔(平方毫米), n 为材料常数。 通过计算得出浇口套管的 表面面积 平方毫米,宽度为 5.8 毫米。进一步计算,底部宽度为 5.9 毫米套管和纸架宽度 为 1.27 毫米。 3.2 循环 分流道 分流道直径计算方式为:部分质量 乘以 密度和部分模具中 心距,公式为 2 4。 D = W x L / 30 (2) 其中, D 是 分流道 直径, W 是 部分 质量, L 是 部分 模具 中心 距。顶套管的体积 从犀牛软件 得出的是 立方毫米 , 重量 0.08 千克所以 主流道 直径为 6.5毫米。进一步计算,套管底部直径为 6.7 毫米,纸架为 1.5 毫米。 3.3 主流道 主流道 尺寸 是由型腔 板的厚度和从给定角度一直径 7 毫米来决定的 。初始冷料井为 7 毫米,基本 冷料井是 10 毫米。图 3 显示了顶部套管,套管位置及底部纸架一起 进料 系统。 图 3 两板模的布局 4填充 分析 - 双板模具 从填充分析结果显示,总填充的时间是 . 秒。在 这阶段 上, 100有两种结果:顶套管短杆 和 塑料不能流到纸架 ,如图 4 所示。 nts 图 填充过程 顶部外壳进行了重新设计,因为前面 结合处 流位于侧 边,而导致熔合线 在该地区的 扩大 ,如图 5 所示。 熔合线是一个流动的结果 ,容易分解成两个单独的 部分。当两方面满足,他们试图重新熔合 到一起,从而导致 形成一个单一的一条线,这 很容易 断裂 5。 图 5 顶部套管的熔合线 4.1 双板模具改造 由于过充,修改浇口尺寸,将 底部外壳减少 25 , 由从 5.9 毫米 降为 4.3 毫米。分流道由 6.7 毫米 降至 至 5 毫米 。纸 架 的位置 由距模具中心 50 毫米到 25 毫米,将分流道尺寸提高 25。 一些凹槽加在 顶 部套壳 表面,以确保塑料 流向顶部套管中心 如图 6 所示 。 nts 图 6 双板模的修正 4.2 修改过的填充过程 从填充改性后分析结果表明 ,塑料熔体三 成分互相平衡。注射 前的总时间为7.804x10-1秒。熔合 线已 消除了顶部 套管中心旁 体,结果是与塑料熔体流向拐角处相交 ,如图 7 所示 。 图 7 修正后的填充过程 5 讨论 该 分流道的纸架的大小 增加, 来转移和 消除 不填充的现象。浇口与底部外壳nts 分流道 分别降低因 为过充 。顶部 套管的上表面 加入 一些凹槽 消除 熔合线。结果是消除了 顶部 套管中心旁体的熔合线 。 从结果中发现,由于是短杆 的问题, 二板模纸架 的浇口和分流道 大小增加了 25, 由于过充问题,底壳的浇口和分流道尺寸减小了 25 。 6 结论 这项研究是在分析两板模中塑料材料的流动是成功的 。做这些 修正改进了型腔的布局和进给系统, 提高了产品质量。此外,塑料制品上的 短杆缺陷 ,过充和熔合线的消除在 的 在 实际模具 中是编造的 。 参考文献 1 S.S.S. Imehezri。, S.M. Sapuan 尔苏莱曼,材料和设计杂志, 26 卷,第157 -166, 2005。 2 L.T. Manzione,计算机辅助工程应用在注塑成型,汉瑟,新 纽约, 1987 年。 3 R.G.W.Pye,注塑成型设计,朗文科学技术,纽约, 1989 年。 4 G. Monges 和 P.Mohren,如何进行注塑模具,汉瑟出版社,纽约, 1993 年。 5 M.B. Douglas,注塑成型,制造工艺基础。学会制造工程师,密歇根州, 1996年。 6 C.T. Wong, S. Sulaiman , N. Ismail,A.M.S. Hamouda,第二世界工程法律程序 国会, Sarawak,马来西亚。 P193-198, 2002。 7 M.Khairol,硕士论文,马来西亚博特拉大学, 2001。 nts 届毕业设计说明书 双盖注塑模具设计 系 、 部: 机械工程系 学生姓名: 指导教师: 职称 讲师 专 业: 材料成型与控制工程 班 级: 成型 完成时间: 6 月 nts 摘 要 本课题主要是针对 塑料 盖的模具设计 ,通过对塑件进行工艺的分析和比较 ,最终设计出一副注塑模。该课题从产品结构工艺性,具体模具结构出发,对模具的浇注系统、模具成型 部分的结构、顶出系统、冷却系统、注塑机的选择及有关参数的校核都有详细的设计,同时并简单的编制了模具的加工工艺。通过整个设计过程表明该模具能够达到此塑件所要求的加工工艺。根据题目设计的主要任务是 塑料 盖注塑模具的设计。也就是设计一副注塑模具来生产盒盖塑件产品,以实现自动化提高产量。 关键词 : 塑料盖;注塑模;模具结构;浇注系统;注塑机 nts ABSTRACT This topic mainly aimed at the mold design of plastic lid. Through the analysis and comparison of the plastic product , the plastic injection mold was designed. This topic came from the technology capability of product, the structure of the mold embarks, the gating system, the injection molding system and the related parameter examination, the mold took shape the partial structures, the against system, the cooling system ,the injection molding machine all had the detailed design, at the same time , the processing craft of the mold were simply established. Through the entire process of the design indicated this mold can achieve the processing craft which the plastic lid requested. Key words: plastic lid; plastic injection mold; the structure of the mold embarks;gating systerm; injection molding machine nts 目 录 前言 . 1 1 塑件成型的工艺性分析 . 4 1.1 塑件的分析 . 4 1.2 PP 的性能分析 . 4 1.3 聚丙烯的成型工艺 . 4 2 注射机的型号和规格选择及校核 . 6 2.1 注射机的选用 . 6 2.2 注射压力的校核 . 7 2.3 锁模力的校核 . 7 3 分型面的选择 . 8 3.1 分型面的形式 . 8 3.2 分型面的选择原则 . 8 3.3 水平分型面的选择 . 8 4 型腔数目的决定及排布 . 9 4.1 型腔数目的确定: . 9 4.2 多型腔的排列: . 9 4.3 模具结构的初步 确定 . 9 5 浇注系统的设计 . 10 5.1 主流道设计: . 10 5.2 分流道的设计 . 11 5.3 浇口的设计: . 13 5.4 校核主流道的剪切速率 . 13 5.5 冷料穴的设计 . 13 6 成型零件的工作尺寸计算 . 14 6.1 凹模的结构形式 . 14 6.2 凸模的结构设计 . 14 6.3 成型零件的工作尺寸 计算 . 15 6.3.1 凹模径向尺寸计算 . 15 6.3.2 凹模深度尺寸的计算 . 16 6.3.3 型芯径向尺寸计算 . 16 6.3.4 型芯高度尺寸的计算 . 17 6.3.5 型腔的壁厚和底板厚度的计算 . 17 nts 7 模架的确定 . 18 7.1 各模板尺寸的确定 . 18 8 导柱导向机构的设 计 . 19 9 脱模推出机构的设计 . 20 9.1 脱模力的计算 . 20 9.2 推出方式的确定 . 20 9.3 脱模机构的设计原则 . 20 10 温度调节系统的设计 . 21 10.1 冷却系统设计 . 21 10.2 冷却时间的确定 . 21 10.3 冷却系统设计原则 . 21 10.4 冷却系统的计算 . 22 11 模具安装 . 23 设计总结 . 24 参考文献 . 25 致 谢 . 26 nts 1 前言 模具被称为工业产品之母。 所以 工业的高速发展也离不开模具工业的不断进步。中国模具巿场规模巨大,随着国内模具工业高速发展,技术也获得了较大的飞跃,但是,仍然面对高档模具以进口为主的尴尬局面。提升技术实力,乃是中国模具工业发展的前途所在。 随着 冲压金 属 制品在机械、电子、交通、国防、建筑、农业等各行业 的 广泛应用,对 冷冲压 模具的需求日益增加, 冲压模在国民经济中的重要性也日益突出。模具作为一种高附加值和技术密集型产品,其技术水平的高低已经成为一个国家制造业水平的重要标志之一。 因此我选择了模具 设计 的课题,即设计 一副能够生产所给 空气滤清器壳的模具,并且结构合理、能保证制品的精度、表面质量。 在设计中 能熟练使用 PRO/E 、AUTOCAD 等 机械、模具相关 绘图软件。 1、 国内方面 发展情况 模具生产技术水平的高低,已成为衡量一个国家产品制造水平高低的重要标志,因为 模具在很大程度上决定着产品的质量、效益和新产品的开发能力。中国经济的高速发展对模具工业提出了越来越高的要求,也为其发展提供了巨大的动力。近 10 年来,中国模具工业一直以每年 15%左右的增长速度快速发展。但与发达国家相比,中国模具工业无论在技术上,还是在管理上,都存在较大差距。特别在大型、精密、复杂、长寿命模具技术上,差距尤为明显。中国每年需要大量进口此类模具,在模具产品结构上,中低档模具相对过剩,市场竞争加剧价格偏低,降低了许多模具企业的效益。而中高档模具能力不足 ,模具的开发能力较弱,技术人才严重不足,科研开 发和技术攻关投入少 等一系列问题,严重制约了中国模具行业的发展。 由于近年市场需求的强大拉动,中国模具工业高速发展,市场广阔,产销两旺。 2003 年我国模具产值达到 450 亿元人民币以上,约折合 50 多亿美元,按模具总量排名,中国紧随日本、美国其后 , 位居世界第三。中国模具 已 涵盖了各种用于金属和非金属成形的特殊装备,被分为 10 大类、 46 小类。 1996 年至 2002 年间,中国模具制造业的产值年平均增长 14%左右, 2003 年增长 25%左右,广东、江苏、浙江、山东等模具发达地区的增长在 25%以上。近两年,我国的模具 技术有了很大的提高,生产的模具有些已接近或达到国际水平。 2003年模具出口 3.368 亿美元,比上年增长在 33.5%,形势喜人。 总的来看,我国技术含量低的模具已供过于求,市场利润空间狭小,而技术含量较高的中、高档模具还远不能适应国民经济发展的需要,精密、复杂的nts 2 冲压模具和塑料模具、轿车覆盖件模具、电子接插件等电子产品模具等高档模具仍有很大一部分依靠进口。 近五年来,我国平均每年进口模具约 11.2 亿美元, 2003 年就进口了近 13.7亿美元的模具,这还未包括随设备和生产线作为附件带进来的模具 。中国现有模具企业超过 2 万家,从业人数 50 多万人。中国的模具生产目前主要集中在华南和华东,大约占了全国模具制造业产值和销售额的三分之二,每年平均增长在 20%左右。 2、国外方面 发展情况 我国模具生产厂中多数是自产自配的工模具车间(分厂),自产自配比例高达 60%左右,而国外模具超过 70%属商品模具。专业模具厂大多是 “大而全 ”、“小而全 ”的组织形式,而国外大多是 “小而专 ”、 “小而精 ”。国内大型、精密、复杂、长寿命的模具占总量比例不足 30%,而国外在 50%以上。 2004 年,模具进出口之比为 3.7 1,进出口相抵 后的净进口额达 13.2 亿美元,为世界模具净进口量最大的国家。 3、 未来 塑料 模具制造技术发展趋势 ( 1)提高大型、精密、复杂、长寿命模具的设计水平及比例。这是由于塑料模成型的制品日渐大型化、复杂化和高精度要求以及因高生产率要求而发展的一模多腔所致。 ( 2)在 塑料模 设计制造中全面推广应用 CAD/CAM/CAE 技术。 CAD/CAM技术已发展成为一项比较成熟的共性技术,近年来模具 CAD/CAM 技术的硬件与软件价格已降低到中小企业普遍 可以接受的程度,为其进一步普及创造良好的条件;基于网络的 CAD/CAM/CAE 一体化系统结构初见端倪,其将解决传统混合型 CAD/CAM 系统无法满足实际生产过程分工协作要求的问题;CAD/CAM 软件的智能化程度将逐步提高;塑料制件及模具的 3D 设计与成型过程的 3D 分析将在我国塑料模具工业中发挥越来越重要的作用。 ( 3)推广应用 热流道技术 、气辅注射成型技术和高压注射成型技术。采用热流道技术的模具可提高制件的生产率和质量,并能大幅度节省塑 料制件的原材料和节约能源,所以广泛应用这项技术是塑料模具的一大变革。制订热流道元器件的国家标准,积极生产价廉高质量的元器件,是发展热流道模具的关键。气体辅助注射成型可在保证产品质量的前提下,大幅度降低成本。目前在汽车和家电行业中正逐步推广使用。气体辅助注射成型比传统的普通注射工艺有更多的工艺参数需要确定和控制,而且常用于较复杂的大型制品,模具设计和控制的难度较大,因此,开发气体辅助成型流动分析软件,显得十分重要。另一方面为了确保塑料件精度,继续研究开发高压注射成型工艺与模具也非常重要。nts 3 ( 4) 开发新的成型工艺和快速经济模具。以适应多品种、少批量的生产方式。 ( 5) 提高塑料模标准化水平和标准件的使用率。我国模具标准件水平和模具标准化程度仍较低,与国外差距甚大,在一定程度上制约着我国模具工业的发展,为提高模具质量和降低模具制造成本,模具标准件的应用要大力推广。为此,首先要制订统一的国家标准,并严格按标准生产;其次要逐步形成规模生产,提高商品化程度、提高标准件质量、降低成本;再次是要进一步增加标准件的规格品种。 ( 6)应用优质材料和先进的表面处理技术对于提高模具寿命和质量显得十分必要。 (7)研究和应用模具的高速测量技术与逆向工程。采用三坐标测量仪或三坐标扫描仪实现逆向工程是塑料模 CAD/CAM 的关键技术之一。研究和应用多样、调整、廉价的检测设备是实现逆向工程的必要前提。 nts 4 1 塑件成型的工艺性分析 本产品主要用于小玩具,它要求质量轻、成本低廉、能大规模的生产、无毒,下列为其图样 图 1 零件图 1.1 塑件的分析 本塑件结构比较简单,生产批量为大批量,根据性能要求,这里选择塑件材料为 PP,塑件的公差按模具设计要求进行转换 。 1.2 PP 的性能分析 1.结晶料,湿性小,易发生融体破裂,长期与热 金属 接触易分解。 2.流动性好,但收缩范围及收缩值大,易发生缩孔 .凹痕,变形。 3.冷却 速度快,浇注系统及冷却系统应缓慢散热,并注意控制成型温度,料温低温高压时容易取向,模 具温度低于 50 度时,塑件不光滑,易产生熔接不良,流痕, 90 度以上易发生翘曲变形。 4.塑料 壁厚须均匀,避免缺胶,尖角,以防应力集中。 1.3 聚丙烯的成型工艺 注塑机选用:对注塑机的选用没有特殊要求。由于 PP 具有高结晶性。需采用注射压力较高及可多段控制的电脑注塑机。锁模力一般按 3800t/m2 来确定,注射量 20%-85%即可。 干燥处理:如果储存适当则不需要干燥处理。 熔化 温度: PP 的熔点为 160-175 ,分解温度为 350 ,但在注射加工时温度设定不能超过 275 。熔融段温度最好在 240 。 nts 5 模具温度:模具温度 50-90 ,对于尺寸要求较高的用高模温。型芯温度比型腔温度低 5 以上。 注射压力:采用较高注射压力( 1500-1800bar)和保压压力(约为注射压力的 80%)。大概在全行程的 95%时转保压,用较长的保压时间。 注射速度:为减少内应力及变形,应选择高速注射,但有些等级的 PP 和模具不适用(出现气泡、气纹)。如刻有花纹的表面出现由浇口扩散的明暗相间条纹,则要用低速 注射和较高模温。 流道和浇口:流道直径 4-7mm,针形浇口长度 1-1.5mm,直径可小至 0.7mm。边形浇口长度越短越好,约为 0.7mm,深度为壁厚的一半,宽度为壁厚的两倍,并随模腔内的熔流长度逐肯增加。模具必须有良好的排气性 ,模具 排气孔深 度为 0.025mm-0.038mm,厚 1.5mm,要避免收缩痕,就要用大而圆的注口及圆形流道,加强筋的厚度要小(例如是壁厚的 50-60%)。均聚 PP 制造的产品,厚度不能超过 3mm,否则会有气泡(厚壁制品只能用共聚 PP)。 熔胶背压:可用 5bar 熔胶背压,色粉料的背压可 适当调高。 制品的后处理:为防止后结晶产生的收缩变形,制品一般需经热水浸泡处理。 nts 6 2 注射机的型号和规格选择及校核 注射模是安装在注射机上的,因此在设计注射模具时应该对注射机有关技术规范进行必要的了解,以便设计出符合要求的模具,同时选定合适的注射机型号。 从模具设计角度考虑,需要了解注射机的主要技术规范。在设计模具时,最好查阅注射机生产厂家提供的有关“注射机使用说明书”上标明的技术规范,。因为即使同一规格的注射机,生产厂家不同,其技术规格也略有差异。 2.1 注射机的选用 选 用注射机时,通常是以某塑件(或模具)实际需要的注射量初选某一公称注射量的注射机型号,然后依次对该机型的公称注射压力、公称锁模力、模板行程以及模具安装部分的尺寸一一进行校核。 经过初步计算 塑件体积: V 塑 =9.9 3 由于浇注系统的凝料在设计之前不能确定准确的数值,但是可以依据经验按照塑件体积的 0.2 倍 1 倍来估算。由于本次设计采用的流到简单并且较短,因此浇注系统的凝料按塑件体积的 0.3 倍来估算,故一次注入模具型腔的塑料熔体的总体积为 V 总 =1.3n V 塑 =1.3 4 9.9=51.48 3 ( 1) 根据一次注入模具型腔的塑料总体积,由 V 公 = V 总 0.8=51.48 0.8=64.35 3根据以上计算,初步选择公称注塑量为 125 3,注塑机选择为 XS-ZY-125型号的注射成型机,其主要技术参数如表 1 表 1 XS-ZY-125 型号的注射成型机技术参数 项目 技术参数 项目 技术参数 螺杆直径 /mm 42 拉杆间距 /mm 260360 理论容量( cm3) 125 最大模具厚度 /mm 300 塑化能力( g/s) 16.8 最小模具厚度 /mm 200 额定注射压力 /Mpa 150 顶杆根数 1 锁模力 /KN 900 定位孔直径 /mm 125 开模行程 /mm 300 喷嘴 球半径 SR/mm 12 螺杆转速 (r/min) 0 200 喷嘴 孔直径 /mm 4 nts 7 2.2 注射压力的校核 该项工作是效核所选注射机的公称压力 P 能否满足塑件所成型时需要的注射压力 P0,其值一般为 70 100MPa, 这里取 P0=100MPa,公称注塑压力 P=150MPa,注射压力安全系数 k1=1.25-1.4,这里取 k1=1.3 k1 P0=1.3 100=130MPa K F胀 F胀 = A 分 P型 ( 2) F锁 注射机的额定锁模力( N); P分 模具型腔内塑料熔体平均压力( MPa);一般为注射压力的 0.3 0.65倍,通常取 20 40MPa。我们这里选 P 型 =30MPa。 K为锁模力安全系数。 A分 塑料和浇 注系统在分型面上的投影面积之和( mm2) 取 A浇 =0.2A 塑 A分 =n(A 浇 +A 塑 )=4 1.2 A 塑 =11424 mm2,由公式( 2)得 F胀 = 11424 30=342.72KN F锁 =900KN,锁模力安全系数 k为 1.1-1.2,这里取 1.2,则 1.2 F 胀=411.26410,所以可将该主型芯视为薄壁塑件。根据参考资料脱模力计算公式为: F=10faE(Tf-Tj)th ( 10) 式中 f为脱模系数取 0.5, a 为塑料的线膨胀系数值为 9.8 10-5/ , E 为脱模温度下塑料的抗拉弹性模量取 1.5 103MPa, Tf为塑料的软化温度取110 ,Tj 脱模时塑件温度取 60, h为型芯脱模方向高度为 17mm,由公式 (10)得 F1=630N (2) 2 R14 小型芯脱模力,因为 R/t=1410,同理由公式( 10)得 F2=1260N (3) 总脱模力 F=F1+F2=1890N 9.2 推出方式的确定 ( 1)采用推杆推出 设 6mm 的圆推杆 4 根,推出面积 A 杆 =(d2 /4) 4=113mm2。推杆推出应力为 F/A 杆 =16.7MPa,查表得许用应力为 12 MPa,应力偏大,不用推杆推出。 ( 2)采用推件板推出 推件板推出面积 A 板 =68 34-66 32=20mm2 推件板推出应力为 1890/200=9.45 MPa 12 MPa 合格 所以采用推件板推出,由于采用侧浇口,充模时容易形成封闭式气囊,因此在每个型芯上设置 1 根直径为 6mm的推杆,以供排气,另外推出更加平稳。 9.3 脱模机构的设计原则 设计脱模机构时,应遵循以下原则: ( 1)结构可靠:机械的运动准确、可靠、灵活,并有足够的刚度和强度。 ( 2)保证塑件不变形、不损坏。 ( 3)保证塑件外观良好。 ( 4)尽量使塑件留在动模一边,以便借助于开模力驱动脱模装置,完成脱nts 21 模动作 。 10 温度调节系统的设计 10.1 冷却系统设计 塑料在成型过程中,模具温度会直接影响到塑料的充模、定型、成型周期和塑件质量。所以,我们在模具上需要设置温度调节系统以到达理想的温度要求。 一般注射模内的塑料熔体温度为 200左右,而塑件从模具型腔中取出时其温度在 60以下。所以热塑性塑料在注射成型后,必须对
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号